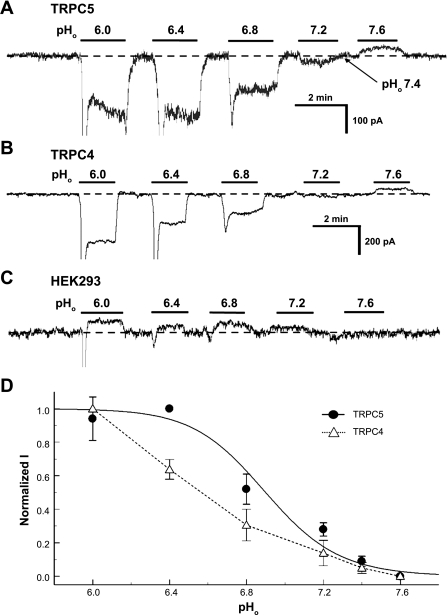
Fig. 4.
Sensitivity of TRPC5 and TRPC4 to pHo. The TRPC channels were expressed in human embryonic kidney (HEK) cells. Whole cell currents were studied in voltage clamp with a holding potential of −60 mV. A: small inward currents were seen in an HEK cell transfected with TRPC5 at pHo 7.4. Extracellular acidifications produced pH-dependent activation of the inward currents. B: similar results were obtained from another cell transfected with TRPC4. Note that the maximum channel activation was not reached at pHo 6.0. C: the same pH exposures did not activate the inward currents in a nontransfected HEK cell. Indeed, the inward currents were slightly inhibited during acid exposures, indicating that the acid-activated currents are mediated by the exogenous TRP channels. D: relationships of pHo vs. TRPC currents (I). The TRPC5 currents were described using the Hill equation with pKa 6.9 and Hill coefficient (nH) 2.4. Similar data fitting was not attempted for TRPC4 as the maximum channel activation was not reached. Despite that, the pHo-current relationship was at least 0.4 pH units lower than that of the TRPC5.