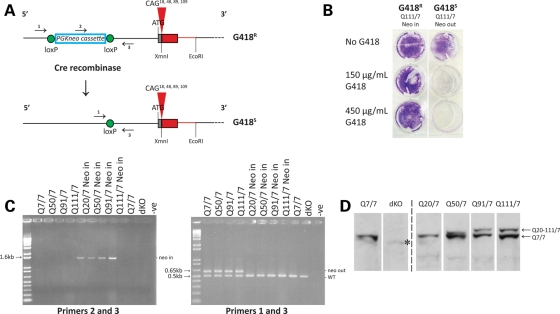
Figure 1.
Generation of an allelic panel of heterozygous CAG knock-in ES cell lines. (A) The upper schematic depicts the targeted Hdh CAG knock-in allele in heterozygous Hdhneo20/7, Hdhneo50/7, Hdhneo91/7 and Hdhneo111/7 ES cell lines, with the location of the loxP-flanked PGKneo selection cassette in the promotor region upstream of the chimeric mouse (gray)/human (red) exon 1 with different CAG repeat sizes (CAG 18, CAG 48, CAG 89 and CAG 109), encoding adjacent CAA, CAG codons, the polyglutamine repeat in the full-length endogenous huntingtin. The corresponding PGKneo-out-targeted allele in the cognate Hdh20/7, Hdh50/7, Hdh91/7 and Hdh111/7 ES cell subclones created by Cre-recombinase-mediated excision is depicted below. Arrows denote the locations of primer sets for ‘neo-in’ (2 and 3) and ‘neo-out’ (1 and 3) PCR amplification assays. The schematic is not drawn to scale. The wild-type allele is not shown. (B) Trypan blue staining reveals the growth of G418-resistant (G418R) Hdhneo111/7 (Q111 neo-in) ES cells and the lack of growth of a subclone of G418-sensitive (G418S) Hdh111/7 (Q111 neo-out) ES cells, derived by Cre-recombinase excision of the pGKneo selection cassette. (C) Agarose gel analysis of PCR amplification products generated by specific PGKneo-in (left gel) and PGKneo-out (right gel) assays. The expected bands confirmed the presence of the PGKneo cassette in the parental Hdhneo20/7, Hdhneo50/7, Hdhneo91/7and Hdhneo111/7 ES cell genomic DNAs (lanes left gel) and the proper removal of the PGKneo cassette from the targeted allele in the cognate neo-out Hdh20/7, Hdh50/7, Hdh91/7 and Hdh111/7 ES cell DNAs (lanes on the left gel). The latter assay also amplifies the expected product from the wild-type allele present in all of the ES cell lines, including the Hdhex4/5/ex4/5 ES cell genomic DNA (dKO), which harbor alleles with a targeted inactivating mutation replacing/deleting exons 4 and 5 (data not shown). PCR products were not detected in genomic DNA minus lanes (−ve) for each assay. (D) The immunoblot, detected with mAb2166, confirms proper expression of both full-length wild-type huntingtin (7 glutamines) and, migrating more slowly, huntingtins from the targeted allele with distinct polyglutamine tracts (Q20, Q50, Q91 and Q111) in protein extracts of Hdh20/7, Hdh50/7, Hdh91/7 and Hdh111/7 ES cells, respectively. Wild-type ES cells (Q7/7) express full-length 7-glutamine huntingtin from both alleles and Hdhex4/5/Hdhex4/5-null ES cells (dKO) express no full-length huntingtin. mAb2166 and other anti-huntingtin antibodies differentially detect the huntingtin with the shorter polyglutamine tract, compared with those with the longer tracts, for reasons that are not yet understood. Bands are ∼350 kDa (the position of the 250 kDa marker is not depicted on this immunoblot). An asterisk indicates a cross-reacting band, previously noted (25).