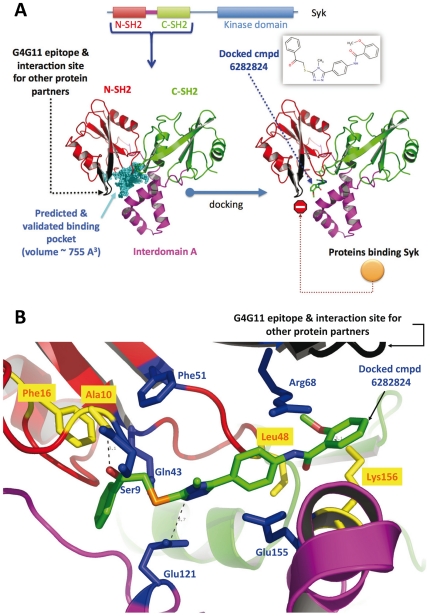
Figure 7. Predicted structure of the complex between compound 6282824 and Syk.
(A) The small molecule was docked into a binding pocket previously identified by our groups and located far away from the catalytic site. We suggest that the mechanism of action for the small molecule involves either or both, small local structural changes in nearby loops thereby impeding appropriate contacts between Syk and some protein partners or that the small molecule directly clashes into upcoming proteins that interact with Syk. (B) Structural analysis of a possible binding pose. A zoom in the binding pocket and rotations were carried out as compared to panel A in order to facilitate the reading of the figure. Side chains mutated in our previous study are shown in dark blue and additional amino acids expected to be important for binding are shown in yellow. The residues found important in our previous mutagenesis study [10] involves Glu 121, Glu 155, and Arg 68. Two hydrogen bonds between the compound and Lys 156 and Ala 10 (backbone N atom) are predicted with a likely electrostatic interaction between Glu 121 and the triazole ring. Hydrophobic, aromatic and pi stacking interactions are also predicted, the main side chains involved are Phe 16, Leu 48, and the hydrophic moiety of the Arg 68 and Glu 155 side chains.