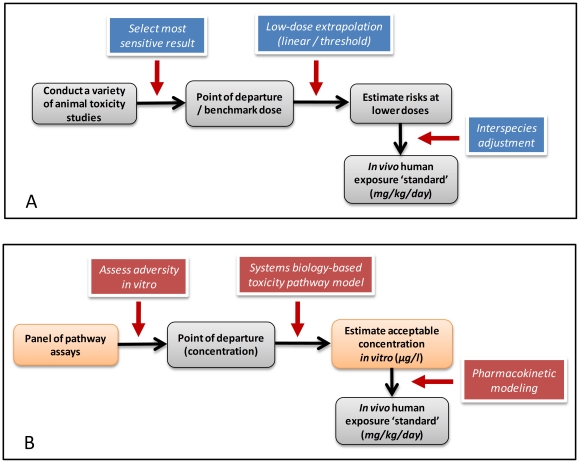
Figure 2. Comparison of current (A) and proposed (B) toxicity testing paradigms.
The current approach (Panel A) to setting regulatory standards involves interpretation of the most sensitive end point observed in animal studies. Low-dose extrapolation requires obtaining a point of departure from the results of the animal studies and the use of either linear or threshold extrapolation plus application of uncertainty factors to the point of departure. Other extrapolations between species or across exposure routes are sometime conducted with pharmacokinetic modeling of the tissue doses that are associated with adverse effects. A similar sequence of steps can be envisioned for setting standards based on pathway assays (Panel B). Likely hazards are determined by the sensitivity of the various toxicity pathway assays; extrapolations require assessing adverse consequences of in vitro exposures and use of computational systems biology pathway (CSBP) and pharmacokinetic modeling to set a standard for human exposure related to mg/kg/day ingested or ppm (parts per million) in the inhaled air.