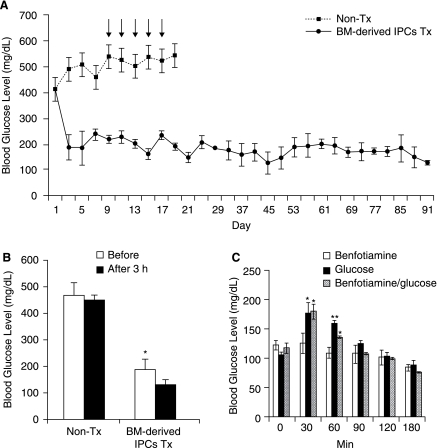
FIG. 6.
Benfotiamine treatment of hyperglycemic mice transplanted with BM-derived IPCs. (A) Blood glucose levels of STZ-treated hyperglycemic NOD/scid mice transplanted with BM-derived IPCs. To ascertain the function, BM-derived IPCs were transplanted into chemically induced diabetic mice and subsequently the changes of blood glucose levels were determined. STZ treated mice were transplanted with saline (non-Tx; n = 4), or transplanted with ∼150 BM-derived IPCs (BM-derived IPCs Tx; n = 4). As seen in the graph, nontreated mice became hyperglycemic and died. (B) Effect of benfotiamine on blood glucose level in benfotiamine treatment of transplanted BM-derived IPCs into hyperglycemic mice. The transplanted and nontransplanted mice were analyzed for blood glucose level before (white bars) and 3 h after (black bars) the benfotiamine treatment (arrows indicated treatment of benfotiamine in Fig. 6A). The data are represented as mean ± SD of blood glucose levels. *p < 0.01 of blood glucose levels compared before and after the treatment of benfotiamine. (C) Blood glucose level in glucose challenge with benfotiamine into normal mice. Glucose challenges were treated 1 g/kg body weight using gavage needle (black bars), benfotiamine alone (blank bars), and glucose with benfotiamine (dotted bars). The data are represented as mean ± SD of blood glucose levels. *p < 0.01 and **p < 0.001 compared with each time point in animals blood glucose level.