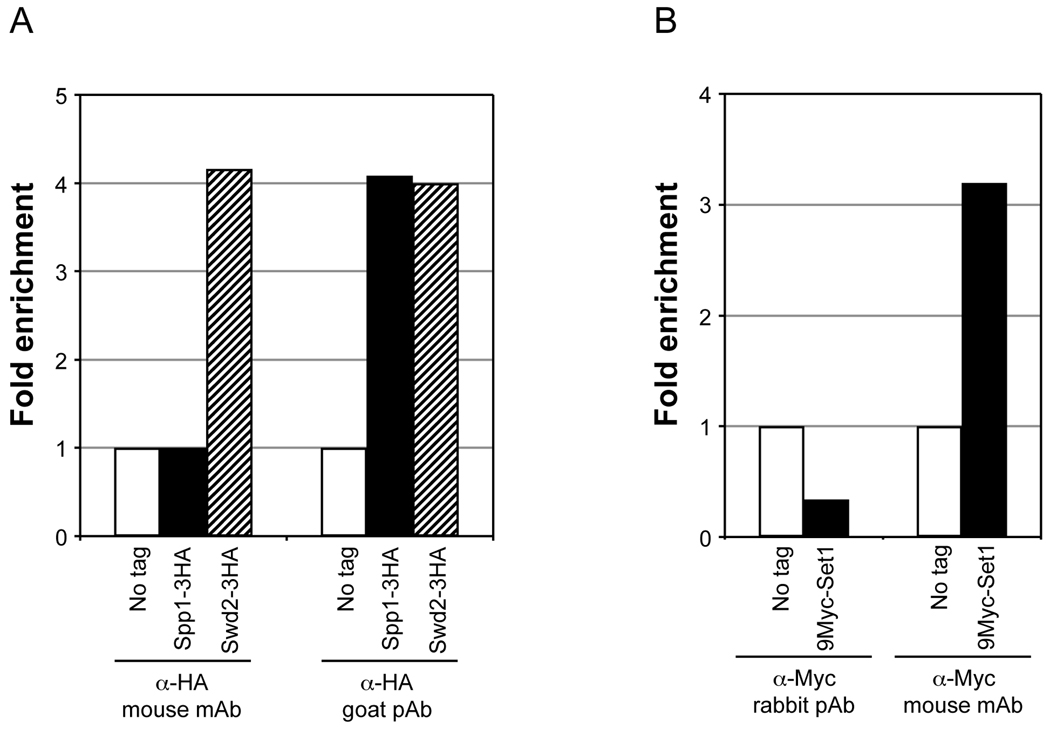
Fig. 3.
Determining the type of antibody suitable for effective enrichment of chromatin-bound factors in ChIP assays. Yeast strains expressing either Spp1 or Swd2 with 3 copies of the HA epitope tag at the C-terminus (Spp1-3HA or Swd2-3HA, respectively), expressing Set1 containing 9 copies of Myc epitope tag at the N-terminus (9Myc-Set1) or strains lacking the tags (no tag) were subjected to double crosslinking (DMA and HCHO) prior to soluble chromatin preparation. For panel A, soluble chromatin (500 µg) was subjected to IP using 2 µl α-HA, which is either a mouse monoclonal antibody (mAb) (kindly provided by Ethan Lee) or goat polyclonal antibody (pAb) (GenScript, catalog no. A00168). For panel B, soluble chromatin (1 mg) was subjected to IP using 2 µl of a mouse monoclonal α-Myc (clone 9E10, kindly provided by Ethan Lee) or a rabbit polyclonal antibody α-Myc (GenScript, catalog no. A00172). Enrichment of ChIP DNA relative to input DNA was calculated following qPCR as described in Fig. 2. Fold enrichment using different types of antibody are shown for Spp1-3HA and Swd2-3HA (panel A) or 9Myc-Set1 (panel B) relative to the no tag control (set as 1).