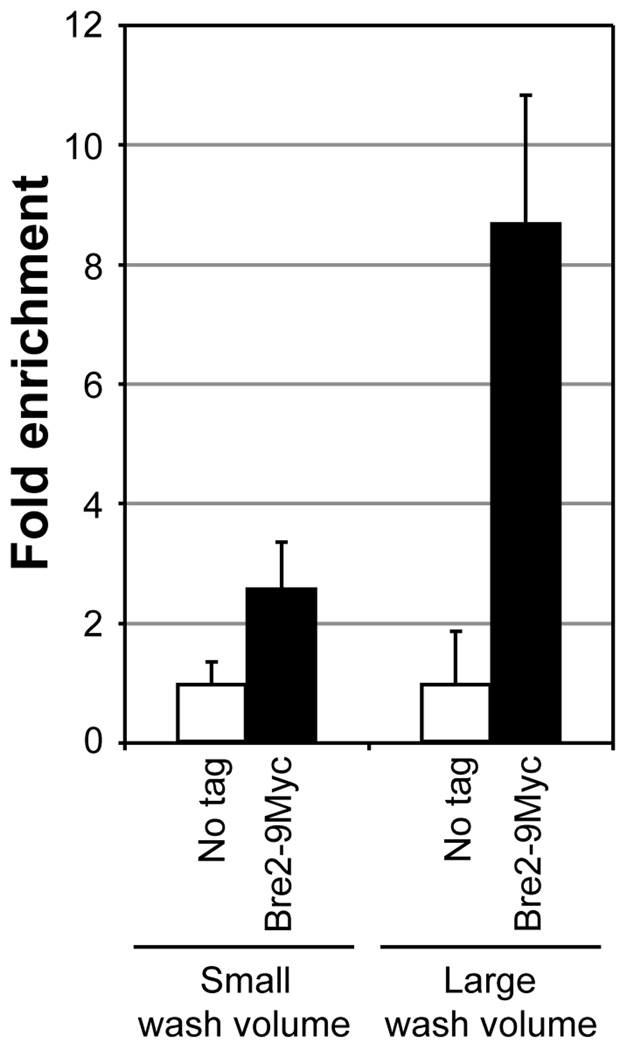
Fig. 4.
Increased washing increases the enrichment of chromatin-bound factors in ChIP assays. Soluble chromatin was prepared using a yeast strain expressing Bre2 with 9 copies of the Myc epitope tag at the C-terminus (Bre2-9Myc) or lacking the tag (no tag) subjected to double crosslinking (DMA and HCHO). 500 µg soluble chromatin was used in IP along with 2 µl mouse monoclonal α-Myc. Following IP, bead-bound immunoprecipitates were washed either with a small volume of buffers [comprised of sequential washes with 500 µl each of FA140 buffer (two times), FA500 buffer and LiCl/NP40 buffer] or a large buffer volume [comprised of sequential washes with 1 ml each of FA140 buffer (two times), FA500 buffer (two times) and LiCl/NP40 buffer]. Enrichment of ChIP DNA relative to input DNA was calculated following qPCR as described in Fig. 2. Fold enrichment using different wash volumes are shown for Bre2-9Myc relative to the no tag control (set as 1).