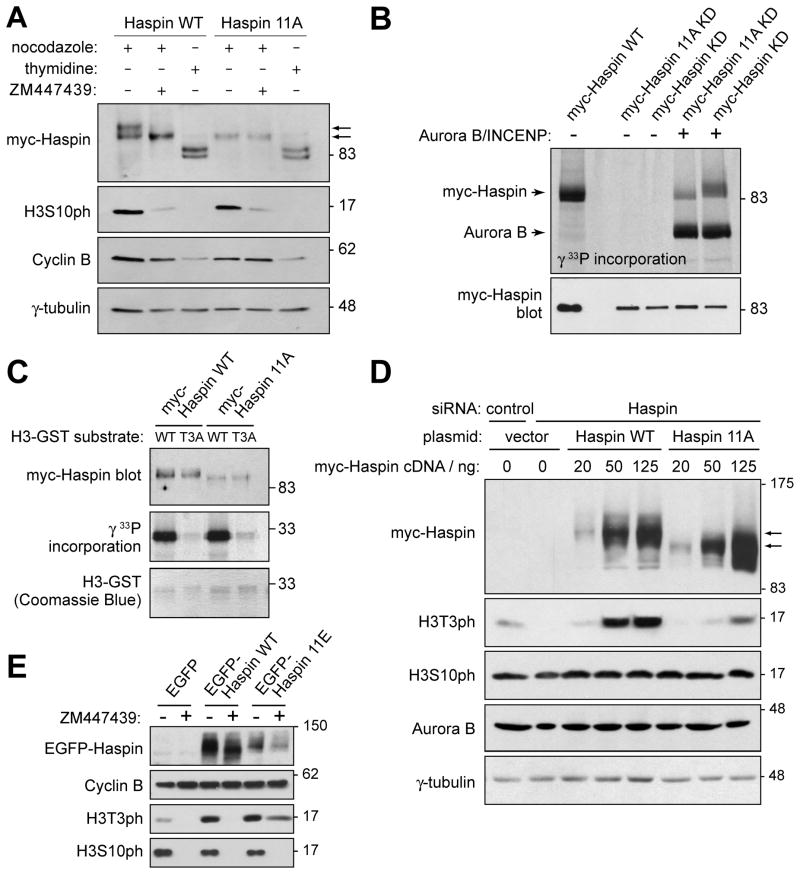
Figure 2. Aurora B indirectly regulates H3T3ph by phosphorylating Haspin.
(A) Myc-Haspin 11A is resistant to Aurora B-mediated phosphorylation in cells. At 19 hr after transfection with myc-Haspin constructs, HeLa cells were blocked at G1/S with thymidine for 18 h, or blocked in mitosis with nocodazole for 3 h followed by a further 3 h in nocodazole with or without ZM447439. Lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting.
(B) Myc-Haspin 11A is resistant to Aurora B-mediated phosphorylation in vitro. Myc-Haspin immunoprecipitates from transiently transfected asynchronous HeLa cells were divided in two and subjected to either phosphorylation in vitro by GST-Aurora B/His-IN with [γ33P]-ATP and analyzed by SDS-PAGE and autoradiography (upper panel) or immunoblotting (lower panel). Kinase deficient (KD) forms of Haspin were used to eliminate autophosphorylation.
(C) The kinase activity of myc-Haspin 11A in vitro is intact. Myc-Haspin WT or myc-Haspin 11A immunoprecipitated from transiently transfected nocodazole-arrested mitotic HeLa cells were exposed to H3(1–45)-GST or H3(1–45)T3A-GST substrates in vitro and analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting (top panel) and autoradiography (middle panel). H3(1–45)-GST was visualized by Coomassie Blue staining (lower panel).
(D) Myc-Haspin 11A is defective in restoring H3T3ph following endogenous Haspin RNAi. HeLa cells were transfected with indicated siRNAs, followed by transfection with various doses of myc-Haspin WT or 11A mutant plasmids. At 24 hr after DNA transfection, cells were blocked in mitosis by nocodazole treatment for 14 hr, and lysates analyzed by immunoblotting.
(E) EGFP-Haspin 11E prevents loss of H3T3ph upon Aurora B inhibition. HeLa cells were transfected with EGFP, EGFP-Haspin WT or 11E plasmids. Cells were released from an 18 h thymidine treatment into fresh medium for 5.5 h and then nocodazole with or without ZM447439 was added for 5.5 h. Finally, MG132 was added for an additional 2.5 h and lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting. See also Figure S2.