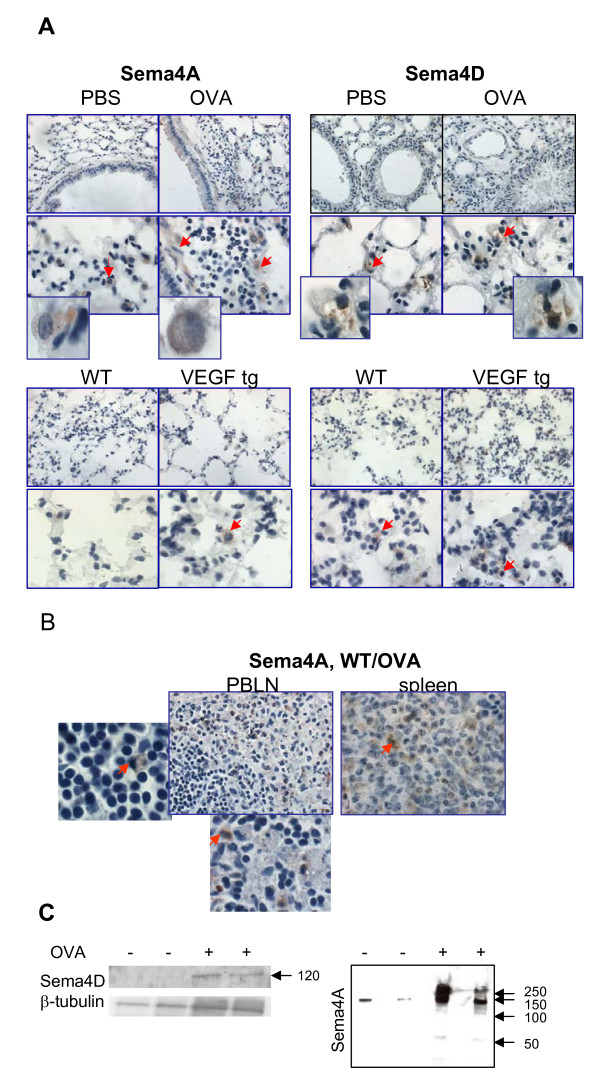
Figure 2.
Lung tissue Sema4A and Sema4D expression and their regulation by allergen and VEGF. (A) Formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded lung tissue sections (top microphotographs) were deparaffinized and immunohistochemistry was performed employing Abs for the intracellular portions of Sema4A and Sema4D molecules. Bottom photomicrographs show immunohistochemistry on frozen lung tissue sections obtained from VEGF tg mice and control WT mice being on DOX water for 7 days. Sema4A expression in PBS-treated lungs was mainly limited to macrophages and dendritic like-cells. Tissue Sema4A expression was upregulated with allergen treatment and VEGF exposure and detected on APC-like cells and smooth muscle cells (both cell types marked with red arrows). Inserts show high magnification fields (100x) with marker-positive cells. Sema4D expression was detected in cell bundle-like shapes (red arrows, inserts) in the lungs obtained from both PBS- and OVA-treated mice. OVA treatment did not significantly modulate tissue levels of Sema4D. (B) Sema4A was abundantly expressed on APC-like cells (inserts, red arrows) in lymphoid tissue of allergen-treated WT mice. (C) Soluble Sema4D protein (120kDa) was detected in lung tissue lysates obtained from OVA-treated mice. Whole Sema4A protein (150 kDa), dimer (>250 kDa), and weak soluble Sema4A (120 kDa) were detected in BAL fluids of OVA-challenged mice. Arrows point to the molecular weight protein standard reference bars.