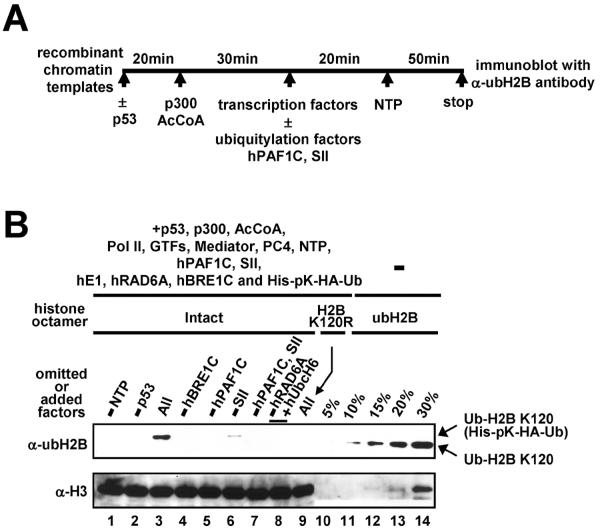
Fig. 5.
Transcription-dependent H2B ubiquitylation. (A) Schematic representation of the standard in vitro transcription assay. Transcription factors included TFIIA, TFIIB, TFIID, TFIIE, TFIIF, TFIIH, PC4, Mediator and Pol II. Ubiquitylation factors included E1, E2 (hRAD6A or hUbcH6), hBRE1C and ubiquitin. Chromatin-based assays also contained the components (ACF1, ISWI and NAP1) employed for chromatin assembly. (B) Transcription-coupled H2B ubiquitylation assays were performed with deletions and additions as indicated (lanes 1–9) and reactions were subjected to immunoblot with indicated antibodies. Histone octamers containing fully ubiquitylated H2B (indicated as % of histone octamers present in the transcription assay) were loaded in lanes 10–14. Part of this figure is reproduced, with permission, from Ref. [12].