Fig. 1.
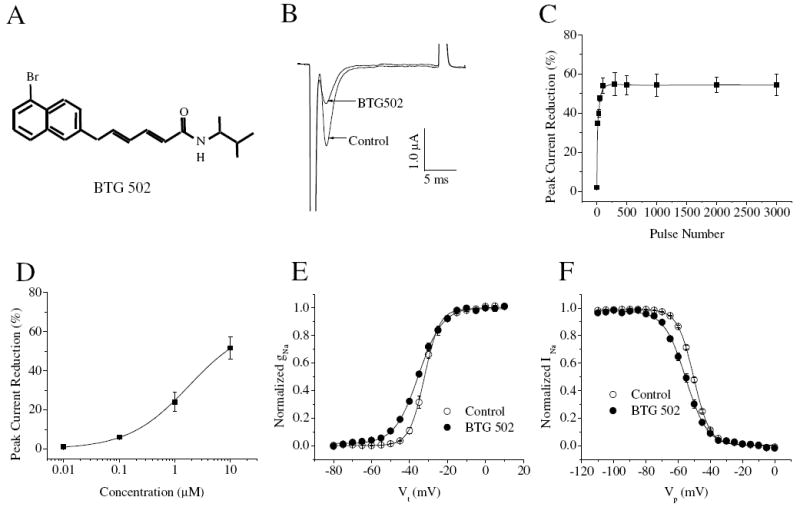
Effects of BTG 502 on the BgNav1-1a channel. (A) The chemical structure of BTG 502. (B) BTG 502 reduced peak sodium current. (C) Use-dependent inhibition of peak current by BTG 502 (10 μM). (D) Dose-response curve of BTG 502 action. (E and F) The voltage dependence of activation (E) and inactivation (F) before and after the application of 10 μM of BTG 502. After 100 repetitive depolarizing pulses at 10 Hz, sodium currents were elicited by a 20-ms test pulse to -10 mV from the holding potential of -120 mV before and after the application of 10 μM of BTG 502. The activation and inactivation curves were fitted with two-state Boltzmann equations.
