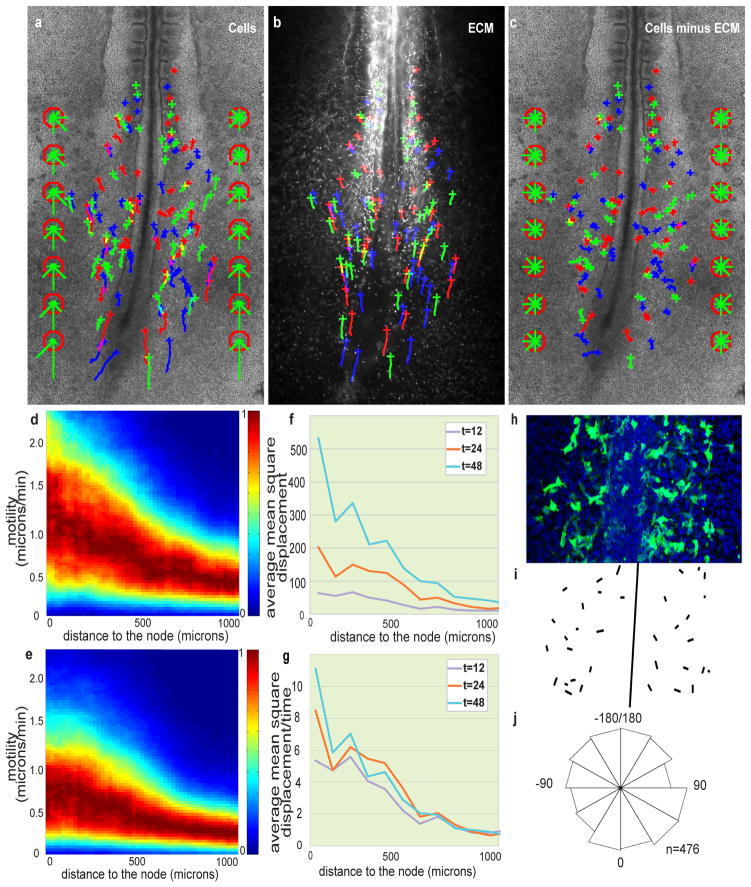
Figure 2. Posterior-to-anterior decreasing gradient of random motility in the PSM.
a–c, H2B-GFP electroporated embryos injected with labelled anti-Fibronectin antibodies. Crosses represent cell position at t = 0; trajectories are represented by green, blue and red lines. The green bars in the red octagons represent cell directionality (see Supplementary Methods). a, Tracking of cellular movements. b, Tracking of ECM movement (Fibronectin). c, Cell movements after subtraction of ECM motion. d, e, Cellular motility along the AP axis with respect to a somite; node position is on the left; normalized probabilities for different motilities are colour coded (see Supplementary Methods). d, Gradient of cellular motility. e, Gradient of cellular motility relative to the ECM. f, Analysis of the mean square displacement of cells relative to the ECM along the AP axis as a function of time (in min.). g, Mean square displacement normalized by time (in min.). h–j, Orientation of cellular protrusions relative to the AP axis. h, Ventral view of the caudal part of an embryo electroporated with membrane-GFP. i, Representation of the orientations of major lamelliform protrusion. j, Rose diagram representing the distribution of the angles between the major cellular lamelliform protrusion and the AP body axis (n = 476 cells from 14 different embryos, 0 degrees corresponds to a protrusion parallel to the AP axis and pointing toward the tail).