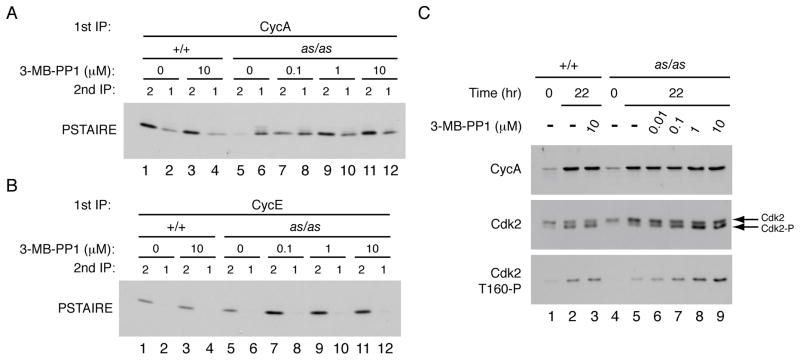
Figure 2. Cdk2as has cyclin A-binding and T-loop phosphorylation defects in vivo.
(A) Wild-type and Cdk2as/as HCT116 cells were treated with DMSO or indicated concentration of 3-MB-PP1 for 96 hr. Cyclin A was immunoprecipitated from extracts and immune complexes were denatured by boiling in 1% SDS. The supernatants were diluted, Cdk1 and Cdk2 were immunoprecipitated, and the amount of each CDK recovered was determined by immunoblotting with PSTAIRE antibody.
(B) Same as (A) except that first immunoprecipitation was of cyclin E.
(C) Wild-type and Cdk2as/as RPE-hTERT cells were synchronized by contact inhibition and released into increasing concentrations of 3-MB-PP1. Amounts of cyclin A, total Cdk2 and Cdk2-Thr160 phosphorylation were determined by immunoblotting—the last both by electrophoretic mobility shift and with Cdk2-Thr160-P specific antibodies.