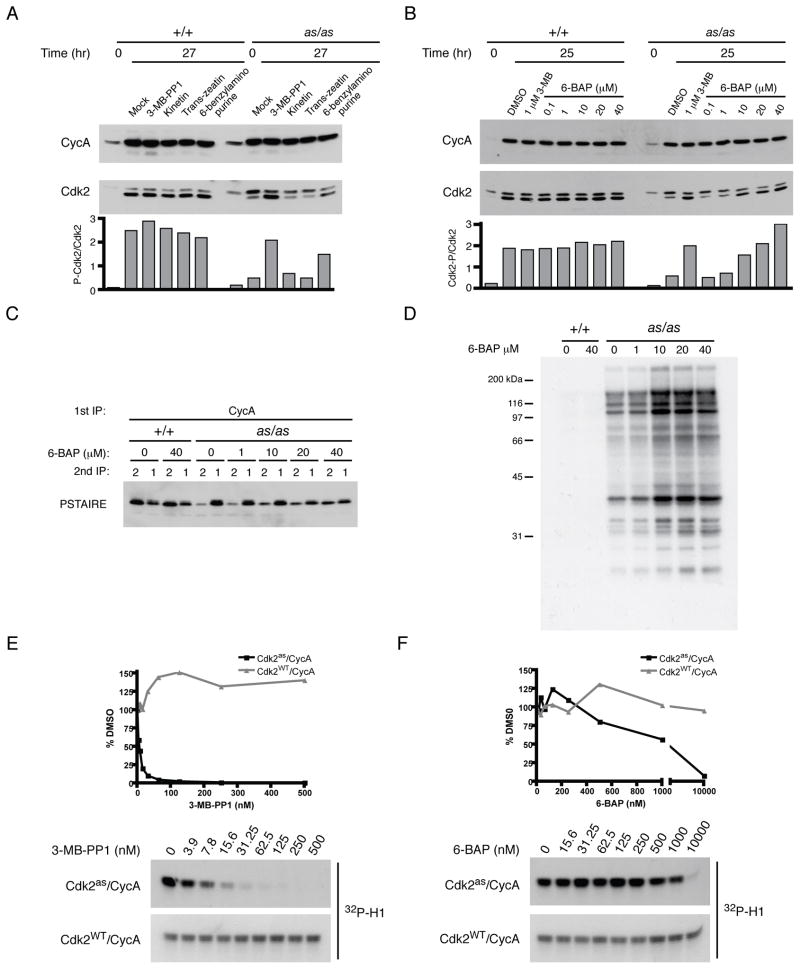
Figure 3. Chemical rescue of Cdk2as by 6-BAP.
(A) Wild-type and Cdk2as/as RPE-hTERT cells were synchronized by contact inhibition and released for 27 hr into medium containing DMSO, 1 μM 3-MB-PP1, or 10 μM of indicated compound. Cyclin A and Cdk2 were detected by immunoblotting, and rescue of Cdk2as was assessed by calculating ratio of phosphorylated-to-unphosphorylated Cdk2 in each extract.
(B) Cells synchronized as in (A) were released into indicated concentration of 3-MB-PP1 or 6-BAP, collected after 25 hr, and phosphorylated-to-unphosphorylated Cdk2 ratio determined.
(C) The ability of 6-BAP to restore normal cyclin A pairing was determined as in Figure 2A.
(D) Extracts from (C) were labeled with [γ-32P]N6-(benzyl)-ATP to determine effect of treating cells with 6-BAP on amount of active Cdk2as in extracts.
(E) Cdk2as/cyclin A and Cdk2WT/cyclin A complexes were tested for sensitivity to 3-MB-PP1 by incubation with increasing concentrations of drug prior to histone H1 kinase assay. IC50 for Cdk2as/cyclin A is ~3 nM.
(F) As in (E) for 3-MB-PP1, IC50 of 6-BAP for Cdk2as/cyclin A was determined to be ~1 μM.