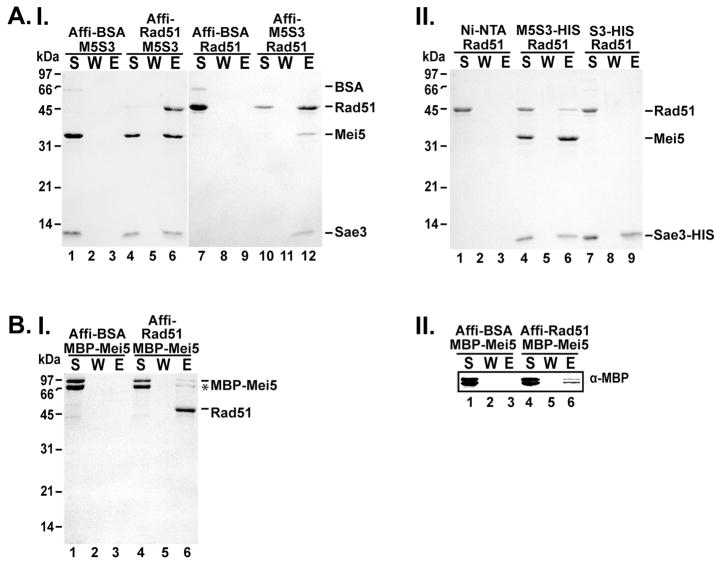
Figure 4. Mei5-Sae3 interacts with Rad51 through Mei5.
(A) Mei5-Sae3 (panel I) was mixed with Affi-Gel containing covalently conjugated BSA or Rad51 (lanes 1–6). Rad51 was mixed with Affi-Gel containing covalently conjugated BSA or Mei5-Sae3 (lanes 7–12). After a wash, the bound protein was eluted with SDS. The supernatant (S), wash (W), and eluate (E) were separated on a SDS-PAGE gel and stained with Coomassie Blue. (A, panel II) Mei5-Sae3 or Sae3-(HIS)6 (panel II) was incubated separately with Rad51. Nickel-NTA beads were added to the reactions and with Rad51 alone with agitation to capture protein complexes. After a wash, the bound protein was eluted and samples were analyzed as described above. (B) MBP-Mei5 (panel I, lanes 1–6) was mixed with Affi-Gel containing covalently conjugated BSA (panel I lanes 1–3) or Rad51 (panel I lanes 4–6). After a wash, the bound protein was eluted and samples were analyzed as described above. Western analysis using anti–MBP antibodies was used to confirm the presence of MBP-Mei5 protein (panel II, lanes 1–6).