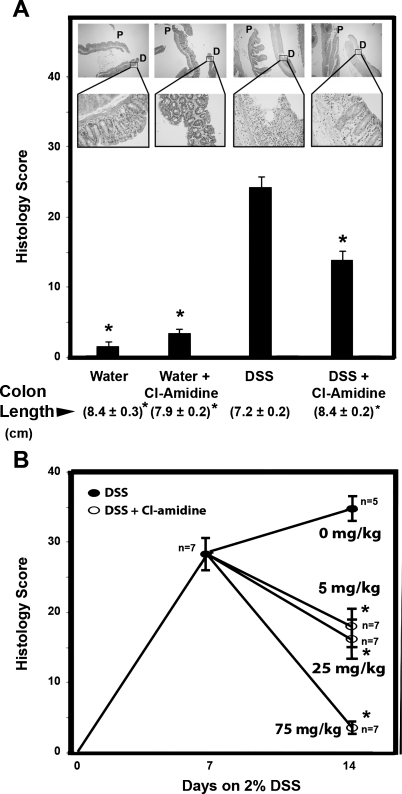
Fig. 2.
Cl-amidine suppresses and reverses DSS-induced colitis in mice. A: histological score is lower in mice injected intraperitoneally with Cl-amidine concomitant with DSS than in mice consuming DSS alone. Values are means ± SE of 10 mice/group for water and water + Cl-amidine (75 mg/kg) and 15 mice/group for DSS and DSS + Cl-amidine. Values in parentheses are colon lengths (means ± SE). *Significantly different from DSS group (P < 0.05). Representative hematoxylin-eosin (H&E)-stained colons are shown for each group [×40 magnification (top) and ×400 magnification (bottom)]. P, proximal colon; D, distal colon. Arrow for the DSS group indicates an area of mucosal ulceration. B: treatment of DSS-induced colitis by Cl-amidine (daily oral gavage) in a dose-response manner. Values are means ± SE for 7 mice each group. *Significantly different from 2% DSS alone (0 mg/kg Cl-amidine corresponds to vehicle alone, which is PBS). For scoring, sections were stained with H&E. Sections were microscopically examined for histopathological and inflammatory changes using a histology scoring system, which consisted of multiplying percent involvement for 3 histological features [inflammation severity (0–3), inflammation extent (0–3), and crypt damage (0–4)] by percent area [0% (0), 1–25% (1), 26–50% (2), 51–75% (3), >75% (4)] of involvement, as previously described (10, 22).