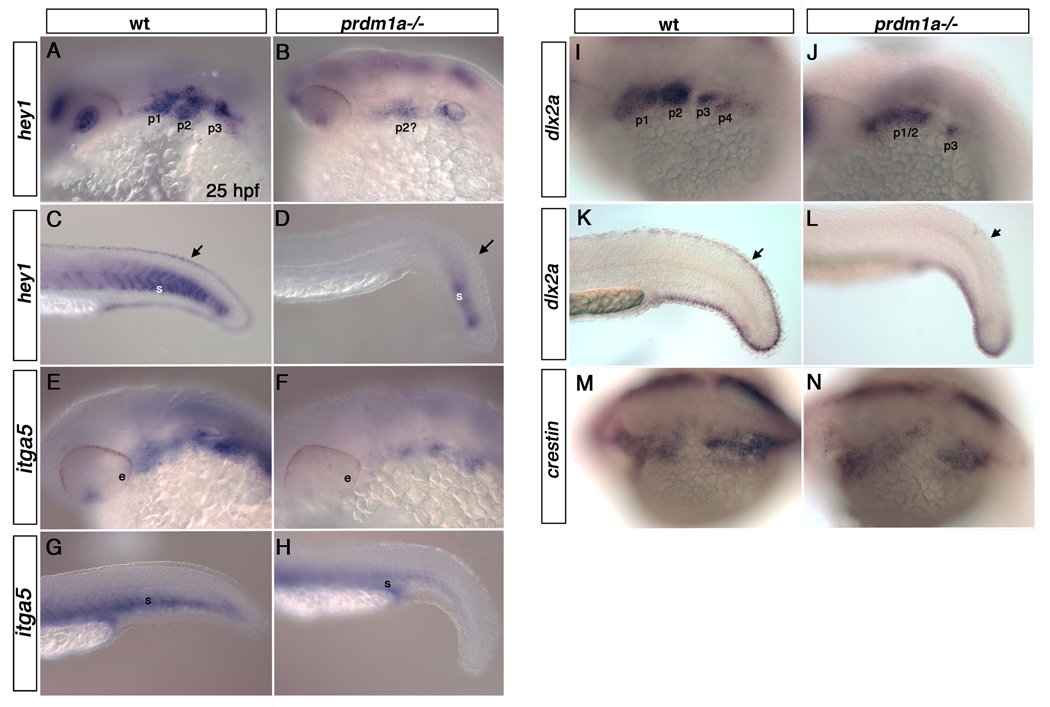
Figure 2. prdm1a mutant embryos exhibit reduced expression of multiple genes within the pharyngeal arches.
Lateral views of wildtype and prdm1a mutant embryos at 25hpf embryos. hey1 is expressed throughout the pharyngeal arches (A) and within the fin mesenchyme and caudal somites (C) of WT embryos at 25hpf, but is reduced in the pharyngeal arches (B), somites and fin mesenchyme (arrows) of prdm1a mutant embryos (D). inta5 is expressed throughout the pharyngeal arches (E) and ventral region of the somites (G) of wild type embryos but is dramatically reduced within the pharyngeal arches (F) and modestly reduced within the somites (H) of prdm1a mutant embryos. dlx2a marks the cranial neural crest cells of the pharyngeal arches (I) and the fin mesenchyme (K) in 25 hpf wild type embryos. prdm1a mutants have reduced expression of dlx2a in the anterior arches and loss of dlx2a in the posterior pharyngeal arches (J). dlx2a is also reduced in the dorsal fin mesenchyme (arrows) of prdm1a mutant embryos (L). crestin expression remains unchanged in the cranial neural crest cells: wild type (M) and prdm1a mutant embryos (N). e, eye; p1, p2, p3,p4, pharyngeal arches 1–4; s, somite.