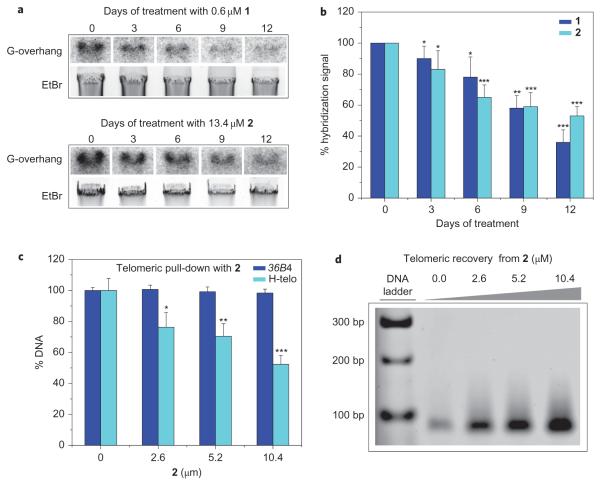
Figure 3. Molecular probe 2 induces in cellulo G-overhang shortening and mediates G-quadruplex-containing telomeric fragment isolation from human cells.
a, Telomeric G-overhang erosion in HT1080 cells on incubation with 1 and 2, as observed by hybridization of a radio-labelled telomeric probe with genomic DNA normalized against ethidium bromide (EtBr) signals. This suggests a direct interaction of the small molecules with telomeric G-quadruplexes. b, Histogram showing the time-course hybridization signal decrease on incubation of HT1080 cells with 1 and 2 (n = 4). c, Percentage of the remaining telomeric sequence and 36B4 control gene in supernatants after pull-down performed on 0.52 μM genomic DNA (n = 5). This shows that 2 interacts selectively with G-quadruplex motifs containing human DNA. d, PCR amplification products of telomeric sequences after DNA recovery from 2, demonstrating that 2 mediates the selective pull-down and release of G-quadruplex-containing DNA. This establishes a direct correlation between G-quadruplex motifs existing at human telomeres and the G-overhang shortening induced by 2. s.d. *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.0001.