Fig. 3. PTB is actively involved in the distribution of CD40L mRNA between the nucleus and cytoplasm.
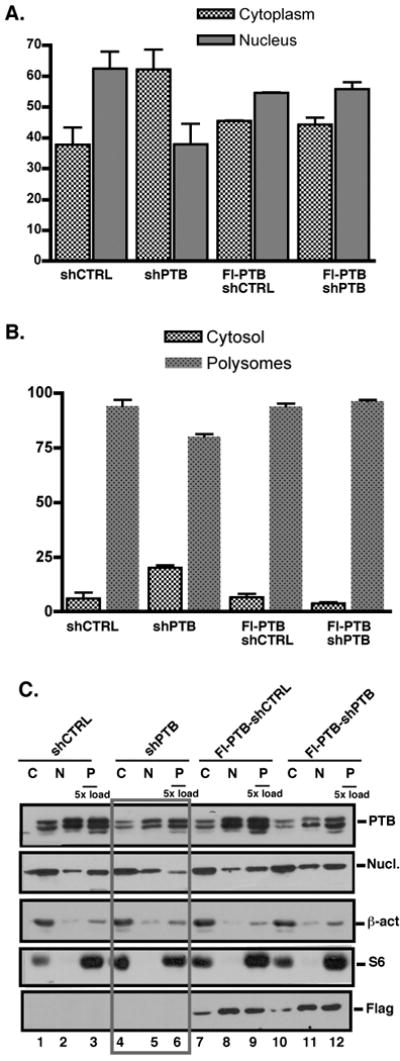
(A). Levels of CD40L mRNA levels in the cytoplasm (grey bars) and nucleus (black bars) of pLV-CTRL and pLV-PTB infected Jurkat/D1.1 and Flag-PTB-Jurkat/D1.1 cells as determined by quantitative PCR. Results represent the Average and SEM of 3 independent experiments. (B) Quantitative PCR analysis of CD40L mRNA from the non-polysomal (white bars) and polysomal (black bars) fractions of pLV-CTRL- and pLV-PTB-infected Jurkat/D1.1 cells and Flag-PTB-Jurkat/D1.1. (C). Western blot analysis using cytoplasmic (2 × 103 cell equivalents), nuclear (2 × 103 cell equivalents) and polysomal (1 × 104 cell equivalents) extracts of Jurkat/D1.1 (lanes 1-6) and Flag-PTB-Jurkat/D1.1 (lanes 7-12) cells infected with pVL-PTB or pVL-CTRL were analyzed for expression of PTB and nucleolin in the different cellular fractions by Western blotting. Membranes were re-probed with antibodies against β-actin and the cytoplasmic ribosomal protein S6 to validate the efficient separation of nuclear, cytoplasmic and polysomal fractions. The membrane was further hybridized with anti-Flag antibodies to confirm expression of the Flag-PTB in the different fractions. Boxed lanes show the effect of PTB downregulation on the different proteins, in particular PTB and nucleolin.
