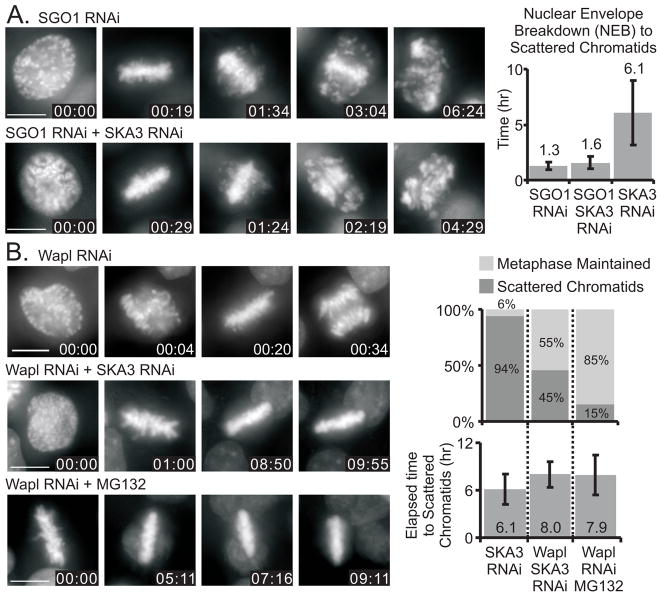
Figure 4.
Manipulating cohesin levels on chromosomes affects the timing of chromosome scattering. (A) Upper panels: HeLa H2B-GFP cells depleted of SGO1 to reduce cohesin levels on mitotic chromosomes achieve metaphase alignment and then separate chromatids with an average duration from nuclear envelope breakdown (NEB) to scatter of 1.3 ± 0.3 hours. Lower panels: HeLa H2B-GFP cells depleted of both SGO1 and SKA3 separate chromatids in an average duration from NEB to scatter of 1.6 ± 0.6 hours. For comparison the graph also shows that cells depleted only of SKA3 separate chromatids after metaphase arrest with an average duration from NEB to scatter of 6.1 ± 2.9 hours. (B) Upper panels: HeLa H2B-GFP cells depleted of Wapl proceed through mitosis. Middle and lower panels: Depletion of Wapl inhibits chromatid scattering in SKA3-depleted or MG132-treated cells. In Ska3-depleted cells 94% underwent chromatid scattering. The percentage was reduced to 45% by co-depletion of Wapl, and depletion of Wapl reduced chromatid scattering to just 15% in MG132-treated cells. 6% of cells depleted only of SKA3 maintain metaphase alignment. For Wapl-depleted cells that did undergo scattering, the average time from metaphase to scattering was also increased. Bars = 10 μm, Time = hr:min, Error bars = standard deviation