Fig. 4.
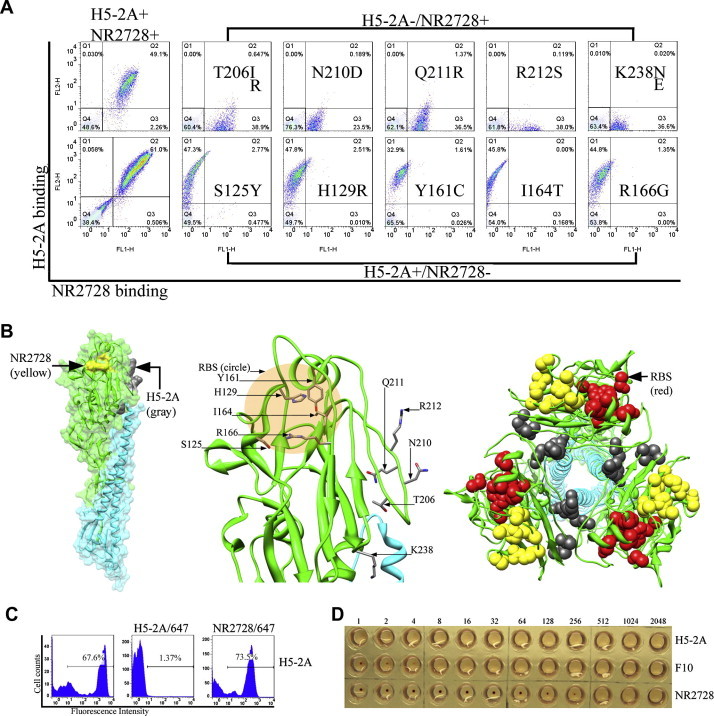
Fine epitope mapping of H5-2A and NR2728 mAbs. (A) FACS profiles demonstrating immunoreactivity of HA1 mutant clones displayed on the yeast surface. Clones with single-point mutations that selectively abolished binding of either H5-2A or NR2728 are shown. (B) Crystal structure of H5 HA0 (PDB 3FKU) with indicated epitopes recognized by H5-2A or NR-2728 mAbs to the HA1 monomer on the yeast surface (left) and a close-up view (middle). Top-down view of the HA trimer 3-fold axis shows the surface-exposed NR2728 epitope (yellow) and cryptic H5-2A epitope (gray) at the trimer interface (right). (C) Competition assay between H5-2A and NR-2728 mAbs. FACS histograms show that pre-incubation of HA with unlabeled HA-2A resulted in self-competition with the Alexa Flour 647-labeled H5-2A, while no competition was detected with the labeled NR2728 for the binding of surface-displayed HA1. (D) HI assay showing strong inhibition ability of NR2728, which was demonstrated above to have a epitope adjacent to the RBS, by blocking virus-mediated hemagglutination. Meanwhile, H5-2A showed no HI activity.
