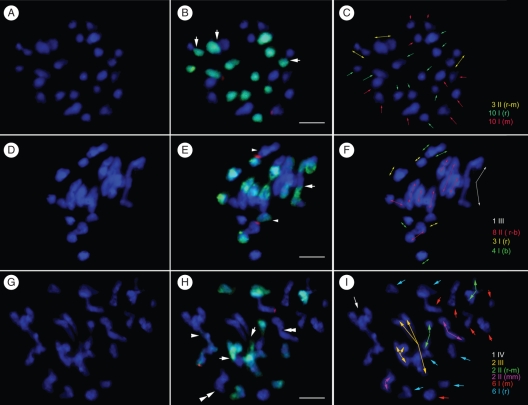
Fig. 3.
FISH and GISH analyses revealed the meiotic chromosome pairing of Paphiopedilum interspecific F1 hybrids. Meiotic chromosomes were counterstained with DAPI in blue (A, D, G). Merged images (B, E, H) showed the chromosomes from P. rothschildianum (in green) and the locations of 45S rDNA loci (in red) of each hybrid. Chromosomes in same/similar configurations were grouped, which were separately indicated by arrows in different colours (C, F, I). (A–C) Chromosome configuration (20I + 3II) at MI of meiosis in the hybrid P. rothschildianum × P. micranthum (2n = 2x = 26). In (B) arrows indicate the bivalents. (D–F) Chromosome configuration (7I + 8II + 1III) at MI of meiosis in the hybrid P. rothschildianum × P. bellatulum (2n = 2x = 26). In (E) arrows indicate the trivalents and chromosomes with 45S rDNA from both parents were separated as univalents (arrowheads). (G–I) Chromosome configuration (12I + 4 II + 2III + 1IV) at MI of meiosis in the hybrid P. rothschildianum × P. moquetteanum (2n = 2x = 30). In (H) arrows indicate the trivalents, an arrowhead indicates the quadrivalent and the double arrowheads indicate two P. moquetteanum autosyndetic pairs. Scale ars = 10 µm.