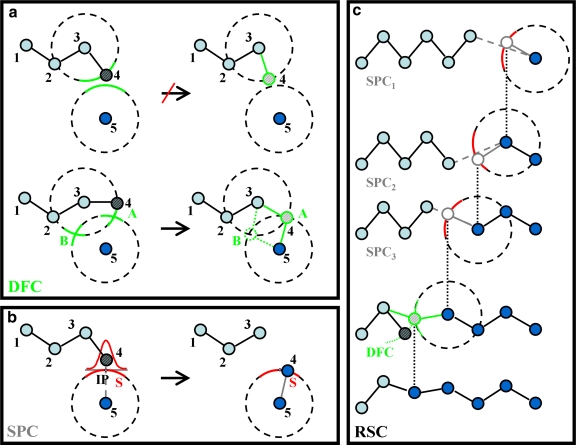
FIG. 1.
(a) Two-dimensional illustration of Deterministic Full Closure (DFC) applied to a five-atom chain r1, … , r5 with a broken bond between atom 4 and 5. If atom 4 is to be positioned by changing the bond angle defined by atoms 2-3-4, then there will either be one favorable solution (marked as point A) or else no solution. (b) Showing Stochastic Partial Closure (SPC) applied to the problem in (a). We mark, S, the red circular arc of constant bond length around atom 5 (a surface in 3D), and IP, the intersection point of the arc S and the line connecting atom 4 to 5. SPC stochastically places atom 4 on arc S based on a normal distribution centered on IP. This method always gives a solution, although it may stretch the bond between atoms 3 and 4. (c) Showing one cycle of Recursive Stochastic Closure (RSC) consisting of three successive, recursive stages of SPC and a single terminating stage of DFC. Circles and lines colored in gray mark atoms and bonds set by SPC, whereas circle and line in green mark atoms and bonds set by the final DFC stage. The figure shows how RSC adjusts bond angles (in 3D, both torsion and bond angles are adjusted), so that the chain break is repaired. The right-most atom is the head atom, which is on the other side of the break; the two left-most atoms belong to the anchor. The other atoms are molten zone.