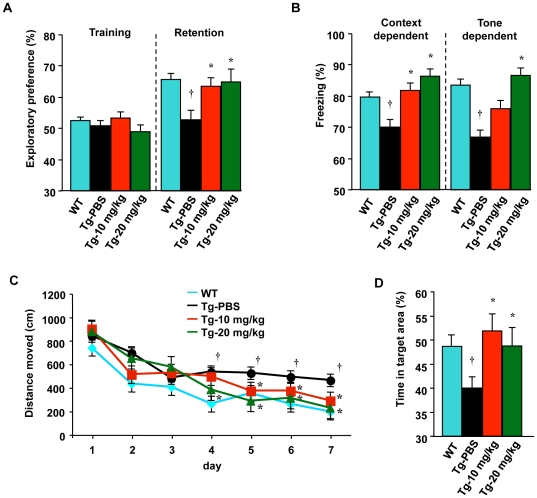
Figure 5. INI-0602 improves memory deficits in APP/PS1 Tg mice.
(A) Object recognition memory assessment by a novel-object recognition test using 9-month-old mice. Data represent the means ± SD (WT, wild-type mice, n = 22; Tg-PBS, PBS-treated Tg mice, n = 22; Tg-10 mg/kg, 10 mg/kg INI-0602-treated Tg mice, n = 16; Tg-20 mg/kg, 20 mg/kg INI-0602-treated Tg mice, n = 15). *, P<0.05 vs. WT; †, P<0.05 vs. Tg-PBS. (B) Associative learning assessment by cued and contextual fear conditioning tests using 10-month-old mice. We assessed the same cohort of mice used in A. Data represent the means ± SD (WT, n = 13; Tg-PBS, n = 13; Tg-10 mg/kg, n = 16; Tg-20 mg/kg, n = 15). *, P<0.05 vs. WT; †, P<0.05 vs. Tg-PBS. (C–D) Reference memory assessment using the distance moved (C) and the percentage of time spent searching (D) during a 60-sec session in a Morris water maze test using 11-month-old mice. We assessed the same cohort of mice used in A. Data represent the means ± SD (WT, n = 22; Tg-PBS, n = 22; Tg-10 mg/kg, n = 16; Tg-20 mg/kg, n = 15). *, P<0.05 vs. WT; †, P<0.05 vs. Tg-PBS.