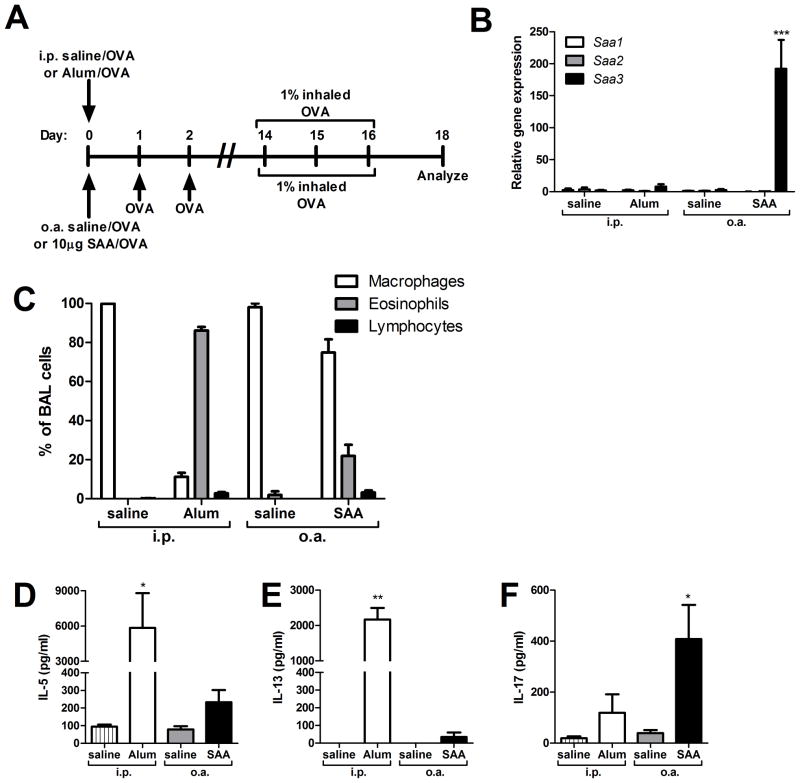
FIGURE 5. SAA inhalation promotes TH17 allergic sensitization.
Mice underwent antigen sensitization via oropharyngeal aspiration (o.a.) with either saline and OVA (saline/OVA) or SAA and OVA (SAA/OVA), or via intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection with either saline and OVA (saline/OVA) or Alum and OVA (Alum/OVA), according to the schema (A). Saa1, Saa2, and Saa3 gene expression in whole lung was measured on day 1, 24 hours after i.p. injection with saline or Alum, or 24 hours after o.a. administration of saline or SAA (B). On day 18, total cell counts from bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluid were performed by hemocytometer and differential analysis was by cytospin (C). On day 18, splenocytes from i.p. saline, i.p. Alum, o.a. saline, and o.a. SAA mice were restimulated in vitro with OVA for 96 hours and IL-5 (D), IL-13 (E), and IL-17A (F) levels in culture media were measured. Data are representative of three independent experiments. * = p<0.05, ** = p<0.005, and *** = p<0.001 compared to saline controls (B, D–F).