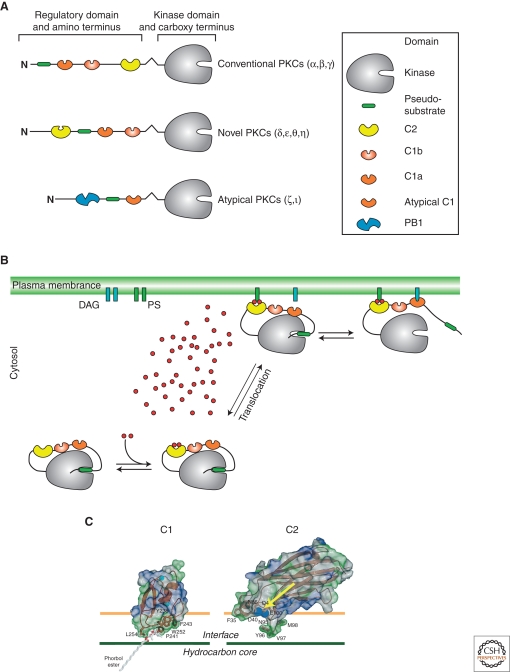
Figure 1.
Basic properties of protein kinases C. (A) The general domain structure of the three subfamilies of the PKCs. The inset explains the symbols used. (B) After maturation and priming steps, activation of the kinase activity involves sequential binding of Ca2+ to the C2 domain, translocation to the plasma membrane, and binding of the C1a domain to DAG. (C) Interaction of the C1 domain with lipids of the plasma membrane (left) is much more intimate than for the Ca2+ (blue spheres marked with an arrow) loaded C2 domain (right). (C, Adapted from Hurley and Misra 2000; reprinted with permission from Annual Reviews, Inc. © 2000.)