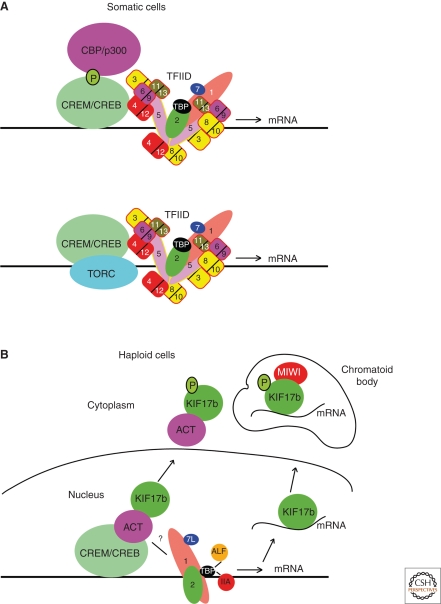
Figure 2.
Schematic model of the CREM-ACT-KIF17b regulatory pathway. (A) In somatic cells, CREB and CREM activate transcription following phosphorylation of a conserved serine residue and recruitment of the CBP and p300 coactivators. CREB and CREM can also interact with TAF4 that is required as a coactivator for their activity. Alternatively, CREB can also activate transcription independent of CBP/p300 via the TORC coactivators. (B) In germ cells, CREM interacts with ACT. At the elongation phase ACT is exported to the cytoplasm by KIF17B to repress CREM activation of target genes. KIF17B also transports mRNAs to the chromatoid body where it interacts with the MIWI protein. Phosphorylation of KIF17B by PKA increases its cytoplasmic localization.