Figure 5.
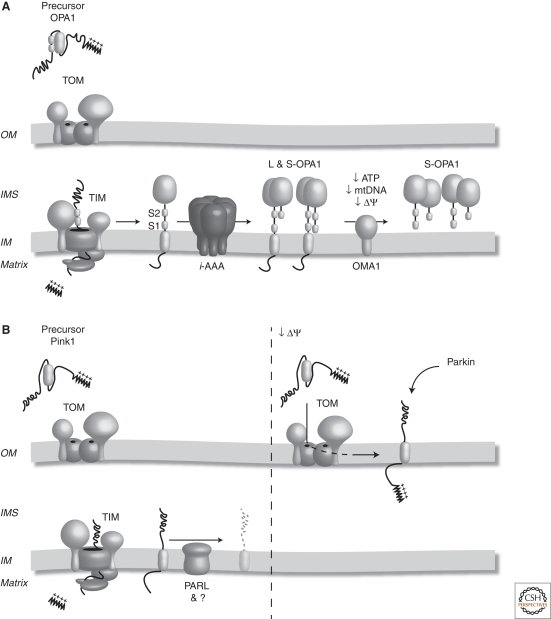
Mitochondrial proteases influence mitochondrial morphology and turnover. (A) OPA1 is synthesized in the cytosol and targeted to mitochondria via its amino-terminal mitochondrial targeting sequence. Following import into the organelle, the targeting signal is cleaved and the hydrophobic transmembrane domain anchors OPA1 in the IM. Following lateral release into the lipid bilayer, OPA1 is subjected to constitutive processing at site 1 (S1) and by Yme1 at site 2 (S2), generating long and short forms of the protein (L and S OPA1) that ensure mitochondrial fusion. Under conditions of mitochondrial dysfunction, including decreased ATP, mtDNA, or membrane potential (ΔΨ), the long OPA1 isoforms are degraded by OMA1, resulting in mitochondrial fragmentation. (B) Pink1 is synthesized in the cytosol with a cleavable mitochondrial targeting sequence. Following its import into the IM, the mitochondrial targeting sequence is cleaved. Pink1 is then processed by PARL and turned over. Under conditions of mitochondrial dysfunction, such as a decrease in membrane potential (ΔΨ), Pink1 is alternately sorted to the mitochondrial OM where it can recruit Parkin to the mitochondrial surface and trigger mitophagy.