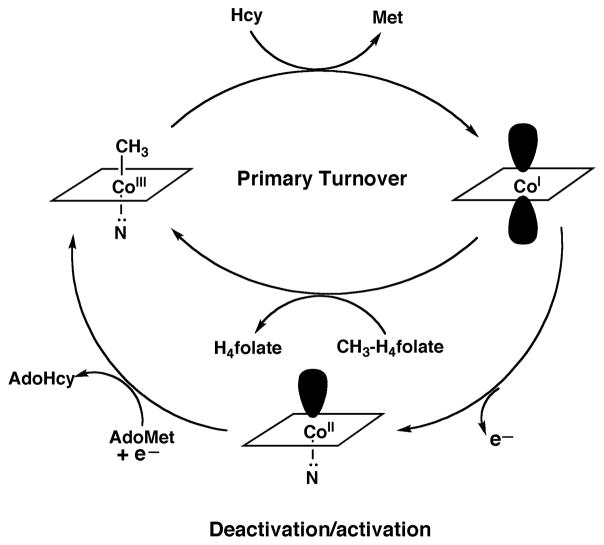
Figure 4. Reactions catalyzed by methionine synthase.
During primary turnover, the enzyme-bound cobalamin cycles between methylcobalamin and cob(I)alamin forms as the prosthetic group is alternately methylated by methyltetrahydrofolate (CH3-H4folate) and demethylated by transfer of the methyl group to homocysteine (Hcy). During turnover under microaerophilic conditions, the cob(I)alamin form of the enzyme is oxidized to cob(II)alamin about once in every 2000 turnovers. This form of the enzyme is inactive, and reactivation requires a reductive methylation in which the reduction of cob(II)alamin to cob(I)alamin is coupled to a highly exergonic methylation using adenosylmethionine (AdoMet) as the methyl donor.