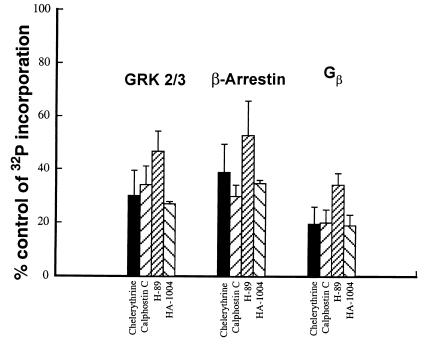
Figure 5.
Kinase inhibitors selective for PKC vs. PKA inhibit the chronic morphine-induced phosphorylation of GRK2/3, β-arrestin, and Gβ. LMMP tissue from the same chronic morphine-treated guinea pig was randomly divided such that 32P incorporation into Gβ-immunoprecipitated protein could be concomitantly determined in the absence as well as presence of kinase inhibitors (added during the last 30 min of the 2-h 32P labeling period). Membranes were prepared and solubilized, and proteins were immunoprecipitated using anti-Gβ antibodies. Immunoprecipitates were subjected to electrophoresis, and radiolabeled proteins were visualized by their concomitant autoradiography (18-h exposure) using storage phosphorimaging techniques. Quantitative densitometric analysis was used to assess magnitude of 32P incorporation into ≈80-, 45-, and 33-kDa signals. Chemical identity of each was assessed as described in Fig. 1. Data are expressed as a percent inhibition of the 32P incorporation observed in the absence of kinase inhibitors. n = 4, 3, 3, and 2 for chelerythrine, calphostin C, H-89, and HA1004, respectively. All reductions in phosphorylation are significant (P < 0.05).