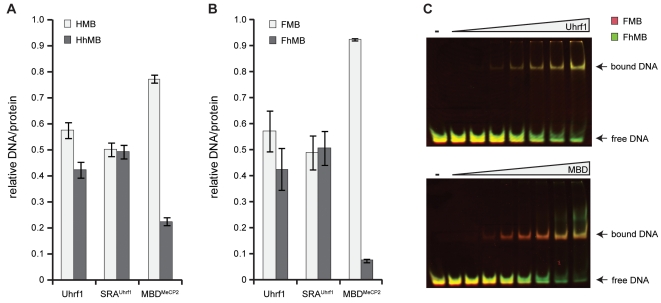
Figure 1. DNA binding specificity of 5-methylcytosine binding proteins.
(A+B) Relative DNA/protein ratios of Uhrf1, its SRA domain (SRAUhrf1) and the MBD of MeCP2 (MBDMeCP2) with two differentially labeled DNA substrates in direct competition. (A) Binding to DNA substrates containing a hemimethylated or hemihydroxymethylated CpG site (HMB versus HhMB, respectively). (B) Binding to DNA substrates containing a fully methylated or fully hydroxymethylated CpG site (FMB versus FhMB, respectively). Results are shown as means of three independent experiments with standard deviation error bars. Note that MBDMeCP2 preferentially binds to FMB, whereas the Uhrf1 constructs do not discriminate between FMB and FhMB. (C) Electrophoretic mobility shift assays were performed with Uhrf1 or MBDMeCP2 and equimolar amounts of FMB (red) and FhMB (green) in competition. The overlay of the two substrate channels reveals simultaneous shifting of both DNA substrates with Uhrf1, whereas with MBDMeCP2 the FMB substrate shifts at a lower protein concentration than the FhMB substrate, confirming differential binding.