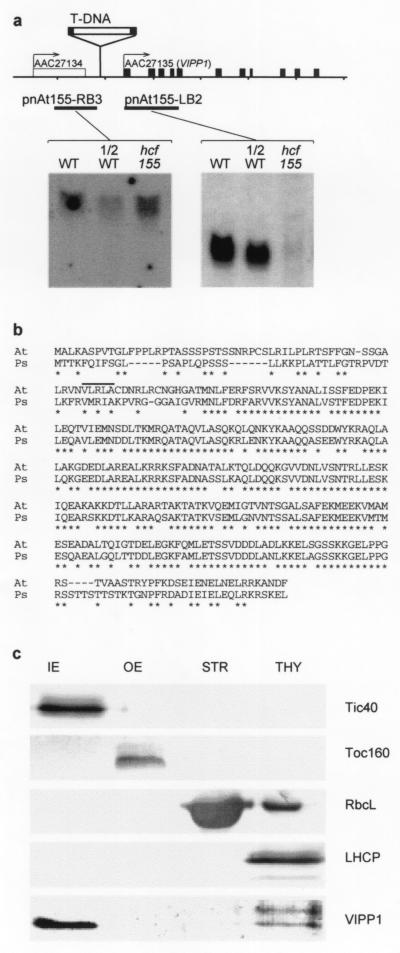
Figure 2.
The T-DNA insertion in hcf155 reduces the expression of a gene [gene designation VIPP1 (AAC27135.1)] that encodes a chloroplast protein that is located in both the inner envelope and the thylakoid membrane. (a) Localization of the T-DNA insertion site and identification of the affected gene by Northern blot analysis. The hybridization probes specific for the AAC27134 and AAC27135 genes that flank the T-DNA insertion were generated by PCR. RNA loadings were 10 μg of total RNA (WT and hcf155) and a 50% dilution in the case of wild-type RNA. (b) Amino acid alignment of the VIPP1/IM30 precursor proteins of Arabidopsis thaliana (At) and Pisum sativum (Ps). The putative cleavage sites are indicated. (c) Localization of the VIPP1 protein in plastid fractions of A. thaliana wild-type plants with the use of marker proteins of established topology: Tic40, subunit of the protein translocation machinery of the inner envelope (IE) (29); Toc160, subunit of the protein translocation machinery of the outer envelope (OE) (16); RbcL, large subunit of the stromal (STR) enzyme ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase; LHCP, major chlorophyll a/b-binding antenna protein of photosystem II, a thylakoidal (THY) protein complex. Equal amounts of protein (8 μg per lane) were loaded onto the gel.