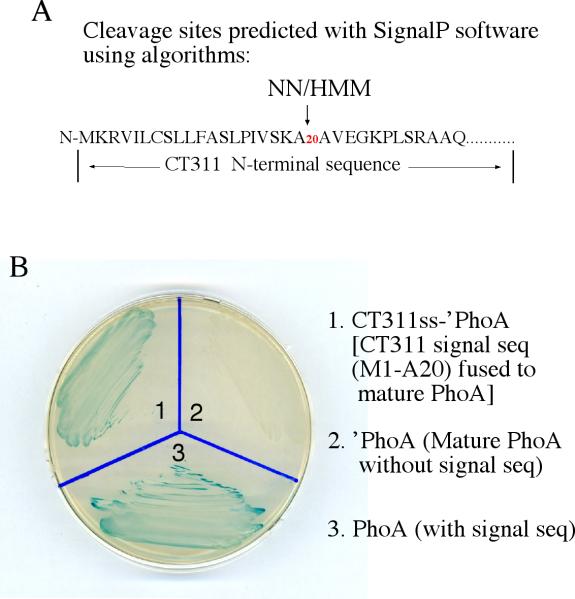
Fig.5.
Prediction and evaluation of N-terminal secretion signal sequence in CT311. The SignalP software was used to identify type II secretion signal peptides (A). Both the NN and HMM algorithms predicted the N-terminal region covering the first 20 amino acids as a signal sequence. The DNA coding for the CT311 signal sequence (CT311ss) was then used to replace the native signal peptide-coding region of the PhoA gene. The chimeric CT311ss-‘PhoA construct was transformed into E. coli for detecting the translocation of PhoA into periplasmic space where PhoA enzymatic activity can be measured in X-gal blue plate. Blue indicates that PhoA has crossed the inner membrane and reached to the periplasm. Note that the bacteria transformed with the full length PhoA (plate slot 1) but not the ‘PhoA missing the secretion sequence (slot 2) turned blue. The CT311ss-‘PhoA chimeric construct-transformed bacteria also turned blue (slot 3), indicating that the CT311 N-terminal 20 amino acid sequence is functional at least in directing the translocation of PhoA to cross the inner membrane. The experiments were repeated twice.