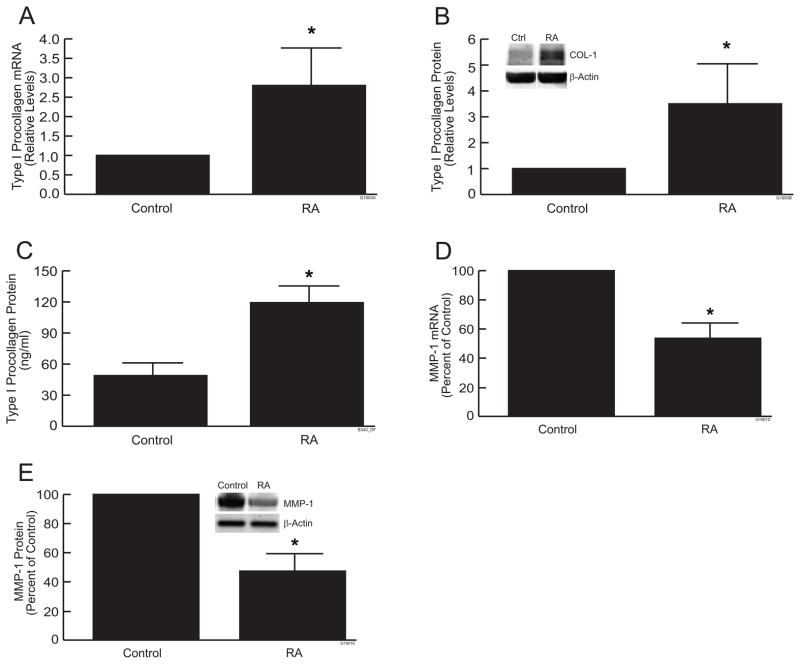
Figure 2.
RA increases type I procollagen and reduces MMP-1 in skin equivalent cultures. Skin equivalent cultures were treated with all-trans retinoic acid (10μM) for 7 days. (a) Type I procollagen mRNA; (b) Type I procollagen protein (Western), (c) Type I procollagen protein (ELISA); (d) MMP-1 mRNA; (e) MMP-1 protein (Western). mRNA levels were quantified by real-time RT-PCR and were normalized to mRNA for 36B4, a ribosomal protein used as an internal control for quantitation. Western analyses were normalized using β-actin as loading control. Inset shows representative Western blots. Secreted type I procollagen (c) in culture medium was determine by ELISA. Data are expressed as mean±SEM, N=3, *p<0.05.