Figure 3.
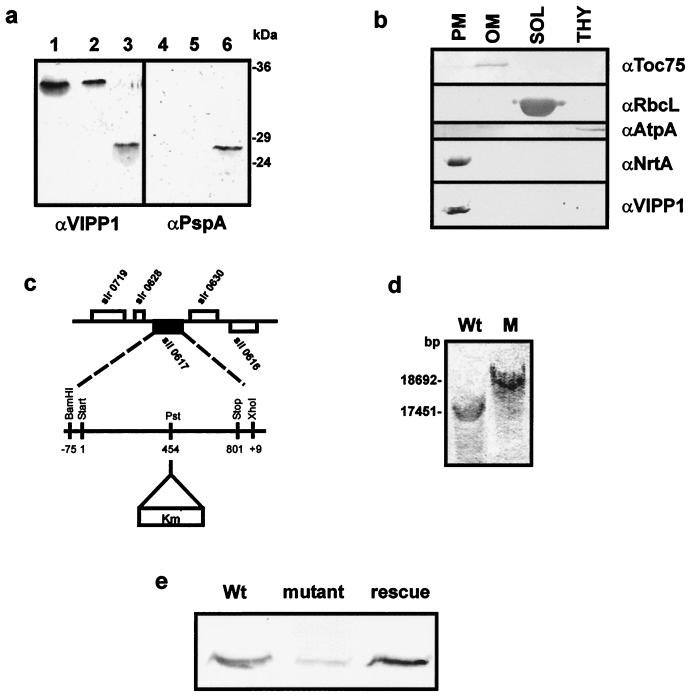
sll0617 encodes a cyanobacterial VIPP1 homologue, and it seems to be located exclusively in the plasma membrane. (a) Immunoblotting with α-VIPP1 and α-PspA antisera identifies VIPP1 in Synechocystis. Lanes 1–3, immunoblot performed with α-VIPP1; lanes 4–6, immunoblot performed with α-PspA; lanes 1 and 4, total leaf extract from A. thaliana; lanes 2 and 5, total protein extract from Synechocystis; lanes 3 and 6, PspA, heterologously expressed in and purified from E. coli. (b) Synechocystis wild-type cells were separated into outer membrane (OM), plasma membrane (PM), cytoplasm (SOL), and thylakoids (THY). Each fraction was analyzed by immunoblotting for the presence of VIPP1. Antisera against the 75-kDa outer membrane protein (α-syn-Toc75), large subunit of Rubisco (α-RbcL), ATP synthase (α-AtpA/B), and nitrate reductase subunit A (α-NrtA) were used as markers for the purity of the different subfractions. (c) sll0617 was disrupted by the insertion of a kanamycin-resistance cassette at position 454 of the coding region. (d) Southern blot analysis was carried out with wild-type and Δsynvipp1 genomic DNA to confirm the disruption of sll0617. (e) Immunoblotting with α-VIPP1 protein establishes an extreme reduction of the level of VIPP1 protein in the Δsynvipp1 mutant compared with wild-type and rescue cells.