Figure 4. The role of the planar cell polarity pathway in cilia formation.
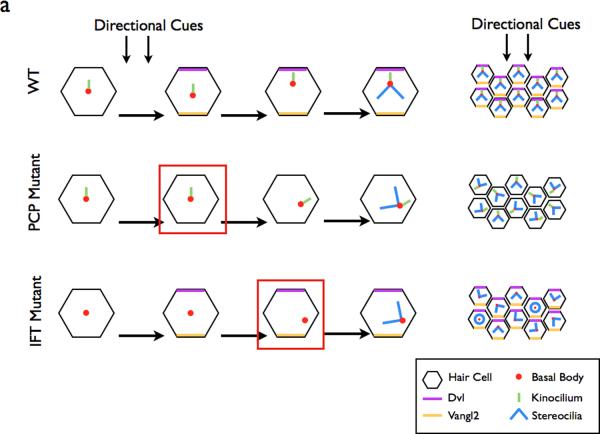
a | In the WT cochlea, directional cues establish localization of core PCP pathway components. The kinocilium then directs the basal body towards the medial side of the cells. This in turn directs the orientation of the stereocilia bundles, resulting in the correct orientation of the bundles within the cochlea. In PCP mutants, the initial cell polarity is never established, resulting in the improper positioning of the basal body and stereocilia. In IFT mutants, planar polarity is established, however the basal body is not repositioned in the absence of the IFT-dependent kinocilium99. Red boxes depict the step in the establishment of ppolarity that is defective in each category of mutants.
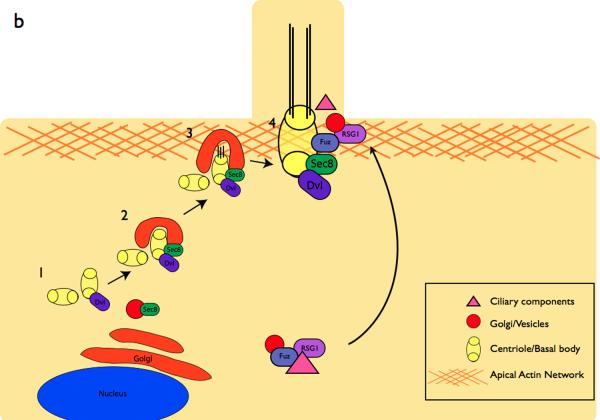
b | Components of the PCP pathway are implicated in cilia formation. The centrioles are initially located away from the cell surface (1)1 where they associate with Dvl, a PCP protein. Sec8, a component of vesicle trafficking machinery is recruited to the basal body in (2)101. At the cell surface in (3), Dvl mediates the fusion of the basal body-associated membrane with the cell membrane101, 134. The axoneme of the cilium extends in (4). In vivo mouse experiments indicate that the PCP effector Fuzzy, together with the small GTPase RGS1, also plays a role in trafficking membrane vesicles and ciliary components to the basal body103.