Fig. 1.
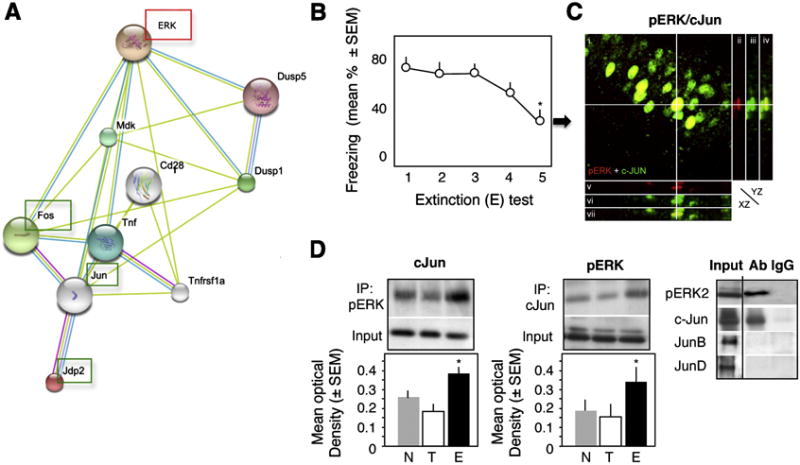
Interaction of pERK and c-Jun during fear extinction. (A) The proposed pathway linking ERK and AP-1 proteins. (B) Extinction of conditioned fear, as revealed by a significant reduction of freezing behavior (F1,4 = 7.23, p < 0.01 vs test 1), after repeated exposure to a context without shock. (C) Co-localization of ERK and c-Jun within hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons 1 hr after the 4th extinction (E) test. i) Confocal image (overlay) of pERK (red) and c-Jun (green) immunofluorescence in CA1. ii-vii) Orthogonal projections along the pERK-positive cell marked with crosshair. ii-iv) Orthogonal projection (YZ plane) of pERK (red), c-Jun (green), and pERK + c-Jun (overlay). v-vii) Orthogonal projection (XZ plane) of pERK (red), c-Jun (green), and pERK + c-Jun (overlay). (D) pERK2 interacts with c-Jun but not JunB or JunD in nuclear extracts of the dorsal hippocampus (left panel). This interaction is significantly stronger in the E (middle and right panels) when compared to the other groups (F2,15 = 11.47, p < 0.001 vs T and N). Statistically significant differences: *p < 0.01 vs test 1.
