Fig. 5.
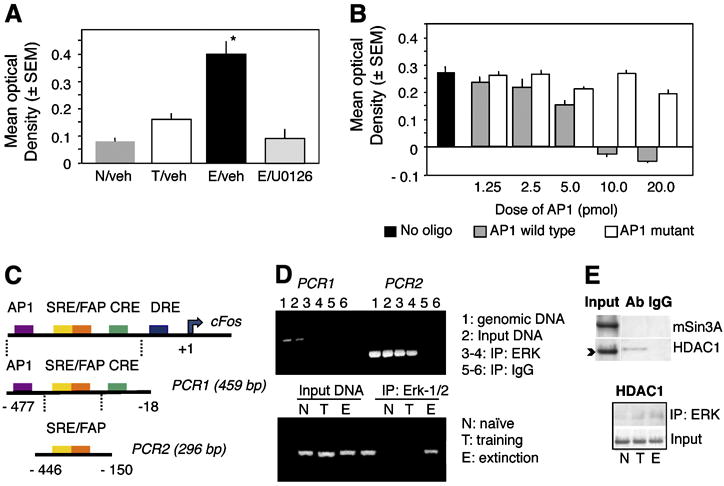
Biding of ERK to AP-1 and the c-Fos promoter. (A) ERK exhibits enhanced binding to the AP- consensus sequence after extinction. (B) This effect is specific because only addition of the consensus but not mutated AP-1 sequence displaces ERK from the immobilized AP-1 oligonucleotide. (C) Schematic representation of the c-Fos promoter. (D) ChIP assays showing amplification of the c-Fos promoter after the nested PCR (PCR2) from genomic DNA, input DNA and DNA co-immunoprecipitated by ERK but not control IgG (right half of the upper panel). PCR1 alone did not yield significant amplification. ERK loaded on the c-Fos promoter only in the E but not N and T groups (lower panel, representative of 6 independent replicates). (E) ERK did not show strong interaction with the c-Fos repressors mSin3A or HDAC1. A slight increase of ERK/HDAC1 (upper panel) was seen both in the T and E groups (lower panel). Statistically significant differences: *p < 0.001 vs all other groups.
