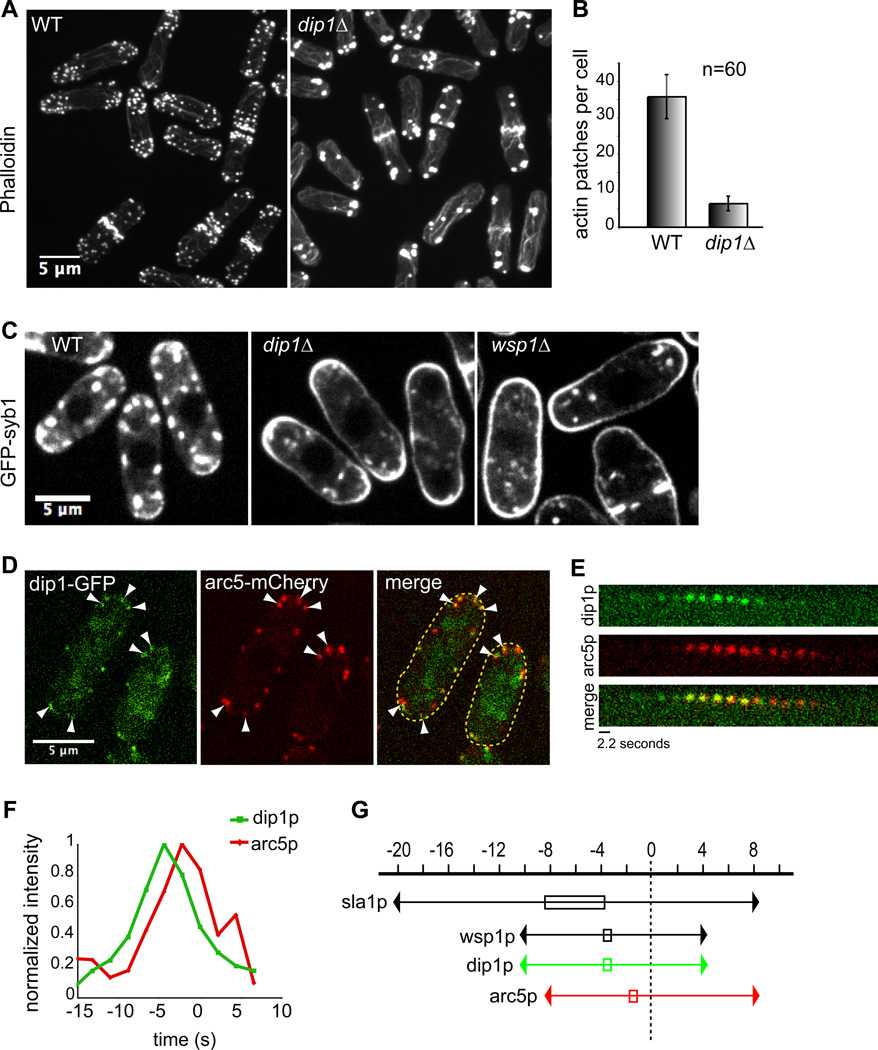
Figure 1. dip1 mutants have defects in actin organization and endocytosis.
(A) AlexaFluor 488-phalloidin stained wildtype (left) and dip1Δ (right) cells. Maximum intensity projections of confocal images are shown. (B) Quantification of the average number of actin patches per cell from images as in A. (n = 60 cells for each strain). Patches within clusters were counted as individuals only if they could be visually distinguished. (C) Images of cells of indicated genotype expressing the integral membrane protein GFP-syb1. GFP-syb1 accumulates at the plasma membrane in endocytic mutants. (D) Dip1p co-localizes with the Arp2/3 marker arc5p in actin patches. Wildtype cells expressing arc5-mCherry and dip1-GFP from their endogenous promoters were imaged in a medial focal plane. White arrowheads indicate sites where dip1p and arc5p co-localize. (E) Time-lapse images of dip1-GFP and arc5-mCherry in a single patch. Arrow indicates patch internalization. GFP and mCherry images were acquired sequentially with exposure times of 2s and 0.2s respectively. (F) Normalized fluorescence intensities of dip1-GFP (green) and arc5-mCherry (red) within a single patch in WT (left). Time = 0s indicates the time of patch internalization. (G) Schematic of dip1p dynamics relative to actin patch proteins sla1p, wsp1p and arc5p. Time = 0s indicates the time of patch internalization. Boxed area indicates time at which protein concentration peaks at the patch. Scale bars = 5µm.