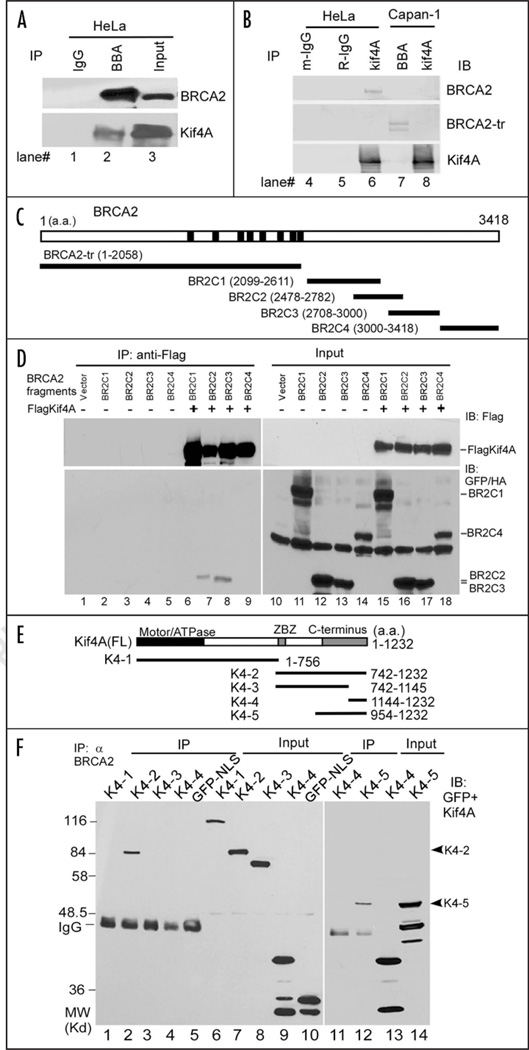
Figure 1.
Kif4A associates with BRCA2. (A and B) Co-immunoprecipitation and immunoblot assays for endogenous BRCA2 and Kif4A. Cells expressing wild-type (HeLa, lanes 1–6) or mutated BRCA2 (Capan-1, lanes 7 & 8) were immunoprecipitated with control IgG (lanes 1, 4 & 5), BBA antibody (lanes 2 & 7) or α Kif4A (lane 6 & 8), and immunoblotted with either BBA to detect the BRCA2 or α Kif4A to detect Kif4A. BRCA2-tr, truncated BRCA2 (~220 KD); m-IgG, mouse IgG; R-IgG, rabbit IgG. IB, immunoblot. (C) Structural illustration of BRCA2 fragments fused with GFP and a T-antigen derived NLS (nuclear localization signal) for mammalian expression. BRCA2-tr was the truncation mutant expressed in Capan-1 cells. (D) Co-immunoprecipitation followed by immunoblot assays for Flag-Kif4A and BRCA2 fragments ectopically co-expressed in HeLa cells. (E) Structural illustration of full length Kif4A and the GFP-tagged Kif4A mutants. ZBZ (amino acids 746–842), leucine zipper/basic/leucine zipper domain. K4-1 is additionally tagged with a NLS sequence since it cannot localize to nucleus by itself. (F) Co-immunoprecipitation assay for BRCA2 and the Kif4A mutants. Kif4A mutants and GFP-NLS were expressed in HeLa cells respectively and the cell extract was prepared for IP. Results were by immunoblot (IB).