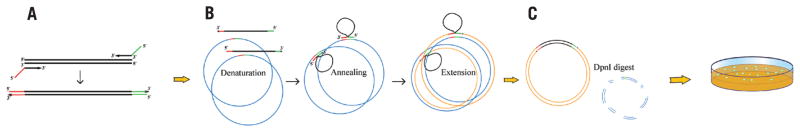
Figure 1. An outline of the overlap extension PCR cloning.
(A) First, the insert is PCR-amplified with the chimeric primers so that the final PCR product has overlapping regions with the vector. (B) Then, vector and insert are mixed, denatured and annealed; the hybridized insert then is extended by Phusion DNA polymerase using vector as a template until polymerase reaches 5′ end of the insert. After several PCR cycles, the new plasmid with two nicks (one on each strand) gets accumulated as a product. (C) The new plasmid can be transformed into E. coli after the parental plasmid is destroyed by DpnI digest.