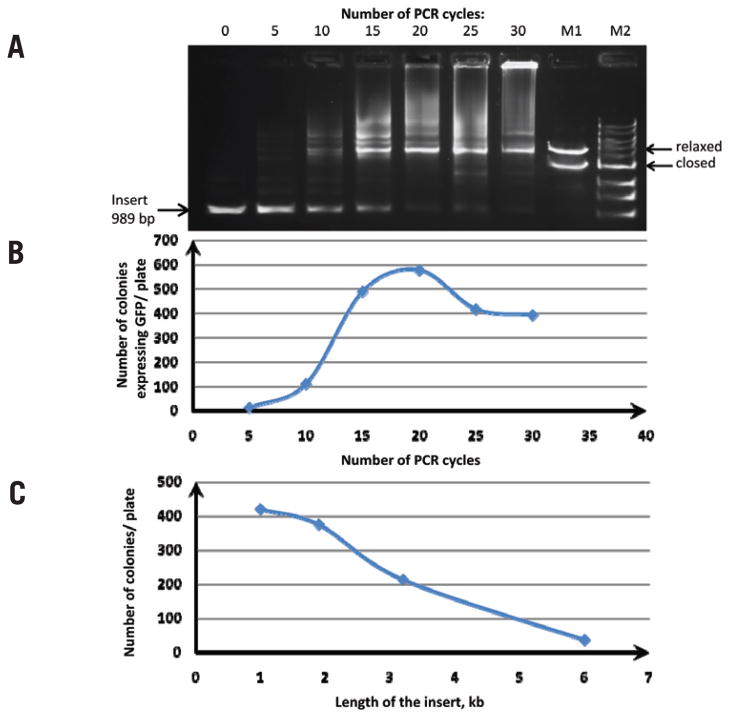
Figure 2. Analysis of the overlap extension PCR cloning reaction.
(A) Products of the overlap extension PCR cloning reaction after 0, 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, and 30 cycles by agarose gel electrophoresis. Three nanograms of pQE30 vector were mixed with 175 ng insert (250 molar excess) in 10 μL total volume; a 4-μL aliquot of reaction was separated on a 0.8% agarose gel. M2, 1 kb DNA ladder; M1, assembled plasmid in closed circular and relaxed circular forms. (B) Overlap extension PCR cloning efficiency of a gfp gene as a function of the number of PCR cycles. Twenty microliters of competent E. coli cells were transformed with 1 μL pQE30/insert overlap extension PCR. The number of green colonies was plotted against the number of PCR cycles for each plate. (C) Overlap extension PCR cloning efficiency as a function of the insert length. Phusion DNA polymerase was used to PCR-amplify products of various sizes: GFP (gfp) gene, β-D-glucuronidase (gusA) gene, β-galactosidase (lacZ) gene, and the luxABCDE operon from the carrying pIMBB plasmid. These products were gel-purified and used in the overlap extension PCR reaction with pQE30 vector. Three nanograms of pQE30 vector were mixed with 175–500 ng insert in a total reaction volume of 10 μL and subjected to 18 cycles of PCR. After DpnI treatment, the overlap extension PCR products were used to transform competent E. coli cells. The number of colonies per plate was plotted against the size of the insert.