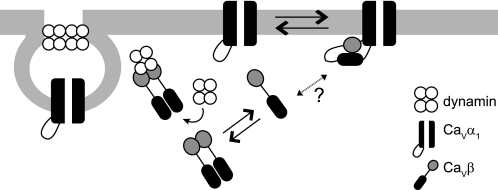
FIGURE 6.
Schematic representation of channel activation and channel internalization by CaVβ. The model illustrates that two different oligomeric states of the protein fulfils two opposing effects on calcium currents. CaVβ binds as a monomer to the AID site of CaVα1 through the GK domain (shown in black) and activates calcium currents. Dissociation of CaVβ weakens intramolecular SH3-GK interactions, making both domains available for further interactions, including dimerization. Association of CaVβ dimers with dynamin, via its SH3 domain (shown in gray), promotes internalization of the channel complex and inhibition of calcium currents through CaVα1. It remains to be determined what triggers dissociation of the β-subunit from its traditional CaVα1 partner. Other ligand proteins may promote the interaction of CaVβ with dynamin.