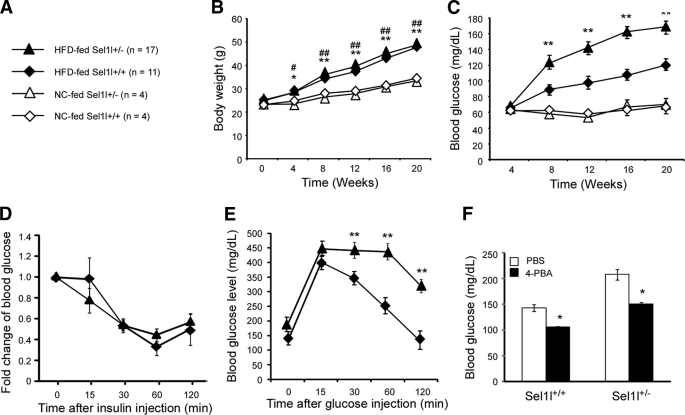
FIGURE 1.
Sel1l+/− mice are susceptible to HFD-induced hyperglycemia. A, shown is a schematic representation of mouse groups and diets. 10-Week-old male Sel1l+/− and Sel1l+/+ mice were randomly divided and fed with NC or a HFD, respectively, for 20 weeks. B, shown are body weight gains of Sel1l+/− and Sel1l+/+ mice on a HFD or NC. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01, Sel1l+/− HFD versus NC; #, p < 0.05; ##, p < 0.01, Sel1l+/+ HFD versus Sel1l+/+ NC. C, shown are fasting blood glucose levels of Sel1l+/− and Sel1l+/+ mice on HFD or NC. **, p < 0.01, Sel1l+/− HFD versus Sel1l+/+ HFD. D, shown is insulin tolerance of Sel1l+/− and Sel1l+/+ mice fed with HFD for 24 weeks. E, shown is glucose tolerance of Sel1l+/− and Sel1l+/+ mice on HFD for 20 weeks. **, p < 0.01, Sel1l+/− HFD (n = 10) versus Sel1l+/+ HFD (n = 11). F, shown are fasting blood glucose levels of Sel1l+/− and Sel1l+/+ mice on HFD for 20 weeks and treated with either PBS or 4-PBA for 1 week; *, p < 0.05 4-PBA versus PBS (n = 5 per genotype). All values are expressed as the mean ± S.E.