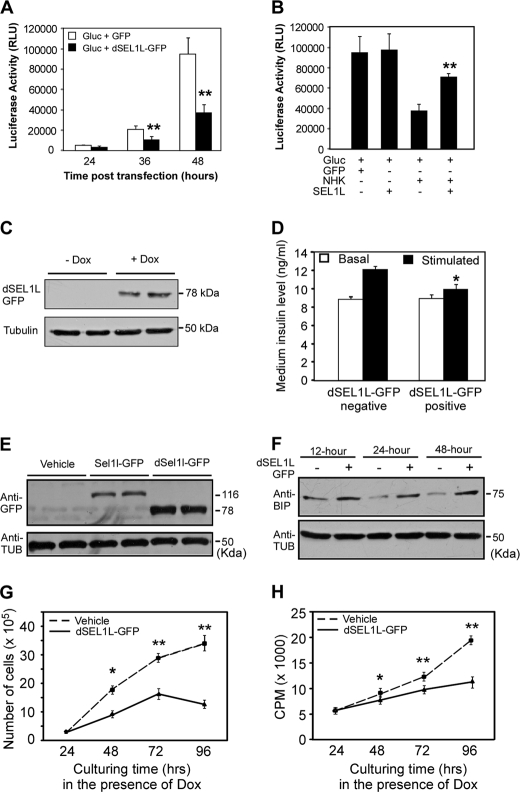
FIGURE 4.
Perturbation of SEL1L function in insulinoma cell lines impairs glucose-stimulated insulin secretion and β-cell proliferation. A, G-luc secretion in Min6 cells transiently expressing a dominant-negative form of SEL1L is shown. Mins6 cells were transiently co-transfected with the indicated expression plasmids. Conditioned media were sampled at 24, 36, and 48 h post-transfection and analyzed by luciferase assay. Expression of dSel1l-GFP markedly suppresses G-luc secretion in Min6 cells. B, G-luc secretion in Min6 cells overexpressing SEL1L. Min6 cells were transiently co-transfected with the indicated expression plasmids. Conditioned media were sampled at 24 h post-transfection and analyzed by luciferase assay. Expression of SEL1L-GFP restores protein secretion inhibited by NHK-GFP. **, p < 0.01. NHK-GFP + SEL1L-GFP versus NHK-GFP- expressing cells. C, shown is an immunoblotting analysis of dSEL1L-GFP fusion protein expression in Min6 cells stably integrated with a Tet-inducible Sel1l-GFP transgene. dSEL1L-GFP was detected using an anti-GFP antibody. Dox, doxycycline. D, GSIS of Min6 cells stably expressing dSEL1L-GFP is shown. *, p < 0.05 dSEL1L-GFP-negative versus dSEL1L-GFP-positive cells. Expression of dSEL1L-GFP markedly inhibits glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in Min6 cells. E, shown is an immunoblotting analysis of SEL1L-GFP and dSEL1L-GFP expression in INS-1 cells stably integrated with Tet-inducible Sel1l-GFP and dSel1l-GFP transgenes. F, shown is an immunoblotting analysis of GRP78/BIP expression in INS-1 cells stably expressing dSEL1L-GFP. Ectopic expression of dSEL1L-GFP in INS-1 cells results in up-regulation of GRP78/BIP. Tub, tubulin G and H, shown are growth profiles of INS-1 cells stably expressing dSEL1L-GFP. Cell proliferation was analyzed through cell counting (G) and by thymidine incorporation assay (H). The data were derived from three independent experiments. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01, vehicle versus dSEL1L-GFP expressing cells. All values are expressed as the mean ± S.E.