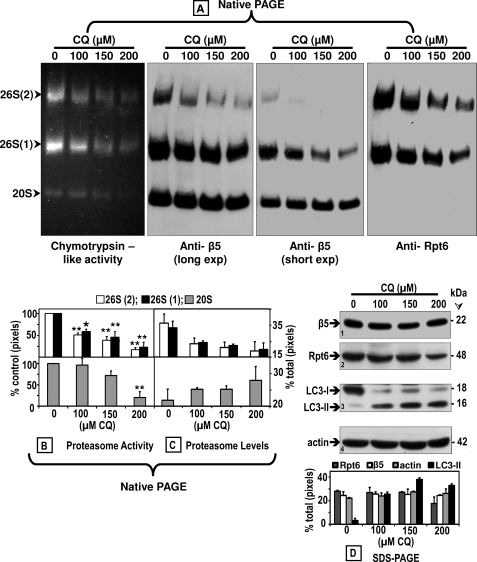
FIGURE 4.
Chloroquine inhibits the proteasome activity and affects its assembly. Crude extracts were prepared from control (0) SK-N-SH cells or cells treated with increasing CQ concentrations for 24 h. Cleared lysates (80 μg/sample) were subjected to nondenaturing gel electrophoresis. A, proteasomal chymotrypsin-like activity was measured with Suc-LLVY-AMC by the in-gel assay (left panel). 26 S and 20 S proteasomes were detected by immunoblotting with an anti-β5 antibody, a subunit of the core proteasome particle (20 S) (two middle panels (long and short exposures (exp))). The 26 S holoenzyme was further identified with an antibody that reacts with the Rpt6/S8 (ATPase) subunit of the 19 S regulatory particle (right panel). Proteasomal 26 S (two capped and one capped) and 20 S forms are indicated by arrowheads on the left. Activity (B) and immunoblot (C) bands on the nondenaturing (native) gel were semi-quantified by densitometry. Data represent total pixels compared with control (no chloroquine) and means and S.E. from three experiments. B, asterisks identify values that are significantly different (*, p at least <0.05; **, p < 0.01) from control (Ct). In parallel experiments (D), cells were harvested for SDS-PAGE followed by Western blot analyses (40 μg of protein/lane) to detect proteasome subunits β5 and Rpt6/S8, autophagy proteins LC3-I and LC3-II, and actin (loading control) after treatment with increasing chloroquine concentrations for 24 h. The level of each protein band was semi-quantified by densitometry (graph). Data represent total pixels and means ± S.D. from duplicate experiments. Molecular mass markers in kDa are shown on the right. The small numbers within the immunoblots designate each row.