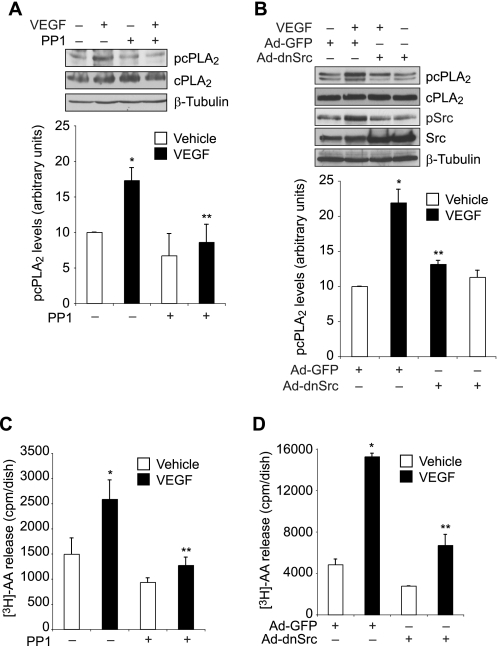
FIGURE 3.
Src mediates VEGF-induced cPLA2 phosphorylation and AA release in HRMVECs. A, quiescent HRMVECs were treated with and without VEGF (40 ng/ml) in the presence or absence of PP1 (10 μm) for 30 min, and cell extracts were prepared and analyzed by Western blotting for cPLA2 phosphorylation using its phosphospecific antibodies. The blot was reprobed sequentially with anti-cPLA2 and anti-β-tubulin antibodies for normalization. B, all conditions were the same as in A except that cells were transduced with Ad-GFP or Ad-dnSrc at 40 multiplicities of infection and growth-arrested before subjecting them to treatment with and without VEGF (40 ng/ml) for 30 min and analyzing the cell extracts for cPLA2 and Src phosphorylation. The blot was reprobed sequentially with anti-cPLA2, anti-Src, and anti-β-tubulin antibodies for normalization or to show overexpression of dominant negative Src. C, HRMVECs that were prelabeled with [3H]AA and growth-arrested were treated with and without VEGF (40 ng/ml) in the presence and absence of PP1 (10 μm) for 1 h, and [3H]AA released into the medium was measured. D, all conditions were the same as in B except that cells were transduced with Ad-GFP or Ad-dnSrc at 40 multiplicities of infection and prelabeled with [3H]AA before subjecting them to treatment with and without VEGF (40 ng/ml) for 1 h and measuring [3H]AA released into the medium. The values are presented as mean ± S.D. *, p < 0.01 versus vehicle control or Ad-GFP control; **, p < 0.01 versus VEGF or Ad-GFP + VEGF.