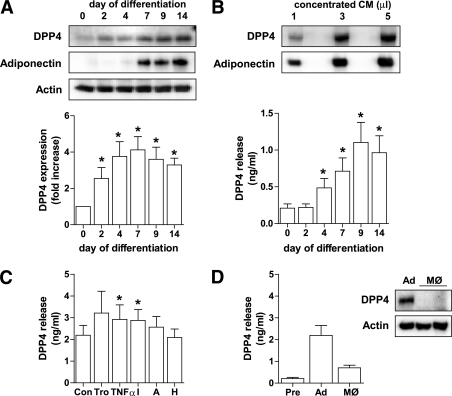
FIG. 1.
DPP4 protein level and release during adipocyte differentiation and after stimulation with different regulatory factors. A: Human primary adipocytes were differentiated as described in research design and methods, and DPP4 protein level during differentiation was analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Western blot. Adiponectin expression served as a control of differentiation. Data were normalized to the protein level of actin and are expressed relative to day 0. Data are mean values ± SEM, n ≥5, *P < 0.05 vs. preadipocytes. B: Detection of DPP4 at day 14 of differentiation using 1–5 μL of concentrated conditioned medium analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Western blot. Twenty-four–hour release of DPP4 by adipocytes determined at different time points of differentiation was analyzed by ELISA. Data are mean values ± SEM, n ≥5, *P < 0.05 vs. day 0. C: Differentiated adipocytes were treated with 5 μmol/L troglitazone, 10 ng TNF-α, 50 mmol/L insulin, 5 nmol/L adiponectin, or incubated under hypoxic conditions for 24 h. DPP4 release by differentiated adipocytes after indicated 24-h treatments as measured by ELISA. Data are mean values ± SEM, n ≥7, *P < 0.05 vs. control. D: DPP4 release by preadipocytes, differentiated adipocytes, and adipose tissue–derived and cultured human macrophages was analyzed by ELISA. Data are mean values ± SEM, n ≥3; 10 μg total lysates derived from adipocytes and macrophages were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Western blot, and signals were detected by enhanced chemiluminescence. A, adiponectin; Ad, adipocyte; CM, conditioned medium; H, hypoxic; I, insulin; MØ, macrophage; Pre, preadipocyte; Tro, troglitazone.