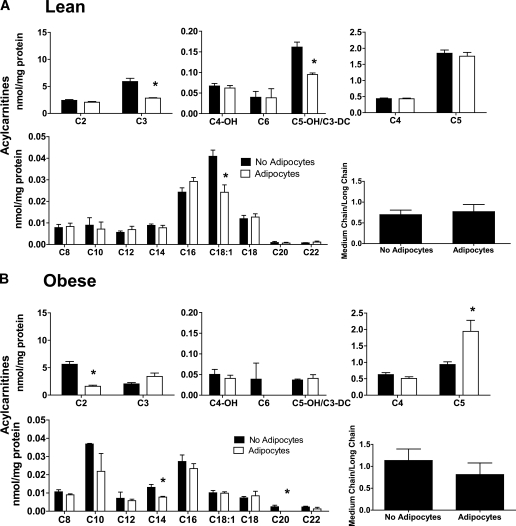
FIG. 4.
Adipocyte exposure alters acylcarnitine accumulation in primary human myotubes. Primary human skeletal myotubes from lean (A) and severely obese (B) women were maintained 24 h in the absence or presence of human adipocytes under basal conditions. After 24 h of coculture, adipocytes were removed, myotubes were washed, and cell lysates were prepared for acylcarnitine profiling by mass spectrometry. C3DC and C5OH are isobaric species. The ratio of total medium-chain relative to total long-chain acylcarnitines was calculated to assess potential flux limitations at the medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase step of β-oxidation. Results are expressed as mean ± SEM and representative of at least three experiments performed in triplicate. Abbreviations reflect carbon chain length (e.g., C2, acetylcarnitine). DC, dicarboxylic acid; OH, hydroxylated species. *Significant (P < 0.05) effect of adipocyte exposure analyzed by Student t test.