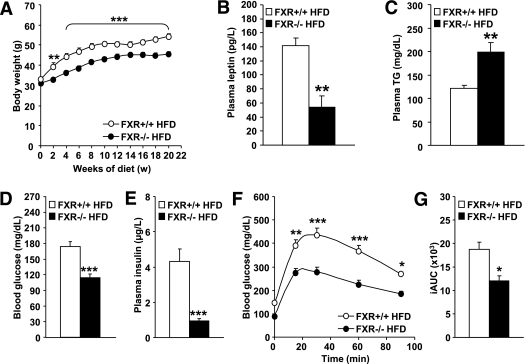
FIG. 5.
FXR deficiency protects from diet-induced obesity and insulin resistance. FXR+/+ (white bars or circles) and FXR−/− mice (black bars or circles) (n = 7–11/group) were fed a HFD for 20 weeks. A: Body weight was monitored weekly (n = 7–11/group). Significance of the overall effect of genotype (P < 0.0001) and age (P < 0.0001) as well as their interaction (P < 0.0001) was calculated by two-way ANOVA. Plasma leptin (B), plasma triglyceride (TG) (C), blood glucose (D), and plasma insulin (E) were determined at the end of the feeding period (n = 4–9/group). Blood glucose excursion (F) and integrated AUC (G) after administration of an intraperitoneal glucose bolus (1 g/kg glucose) were measured at the end of the feeding period (n = 6–9/group). Significance of the overall effect of genotype (P < 0.0001) and time (P < 0.0001) was calculated by two-way ANOVA. Values are means ± SEM. Differences between genotypes over time were analyzed by two-way ANOVA and Bonferroni post hoc test; differences between genotypes were calculated by Mann-Whitney test (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001).